Manual arc welding technology
The connection of metal structures, including pipes, is often done manually. Almost everyone who has welding skills can do it on their own. It is only necessary to carefully understand the features of a particular work.
Special features
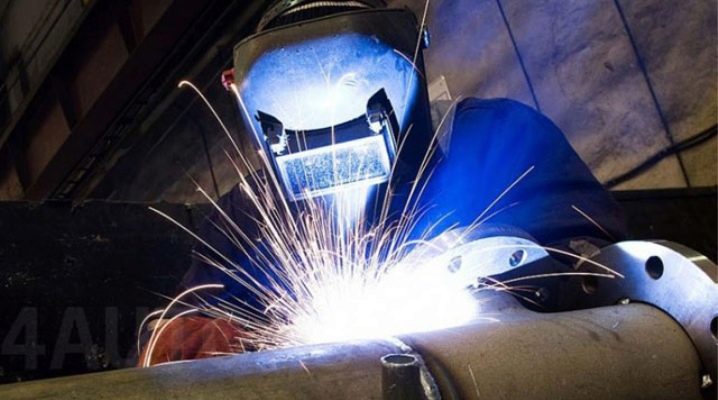
Manual arc welding of pipes implies a strong warming up at the site where the electrodes are applied. After all, it passes through a powerful discharge (arc). It melts the metal and causes its drops to flow downwards, to the place where the pipeline elements are connected. Their surface layers inevitably melt, but at the same time, droplets that come from above lose heat and freeze. They make the seam tight and provide docking parts.
Important: the metallurgical slag present in the electrode is in the upper part of the melt until it hardens.
The undoubted advantages of electric arc technology are:
- simplicity (this work is beyond the power of any qualified welder);
- reliable sealing of the formed seams;
- mechanical strength of the metal bond.
How to prepare?
Welding of large-diameter pipes, such as on gas mains, is carried out using electrodes coated with a film of cellulose. If you need to connect the corner seams and make the so-called tack, use elements with an outer layer of rutile. The most complex manipulations are carried out by electrodes combining the two specified types of elements. In addition to such parts and welding machines, rectifying transformers will be required. However, experienced professionals advise the use of inverters.
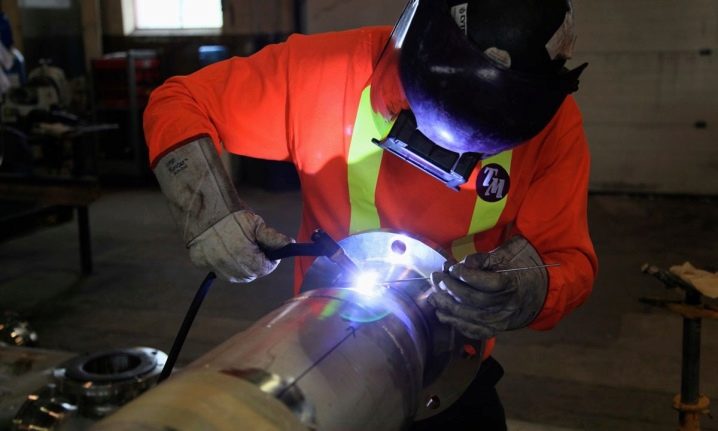
Among welding machines, systems are preferred that allow metal to be processed in various modes.. But among them there must be one that will help to weld a certain steel grade in pipes of a given thickness. The quality of the resulting joint is primarily determined by the electrodes and the tuning technique. The capabilities of welding systems are about the same, and the share of frankly substandard among them is small.Previously, as with other connection methods, it is necessary to remove any dirt and oil stains.
Components of the future or repaired pipeline put the joint to the junction and as much as possible align. After setting up the welding mode and securing the required electrodes, they put contacts on the pipes, which provide grounding. Mitts can increase the reliability of future contacts. So called small seams, ensuring the exact placement of parts to be attached. When they are formed, the serious work begins.
Recommendations
In addition to the standards established by GOST, it is required to take into account the long-term practice of welders. From it follows that the launch of the apparatus should occur immediately with a light touch of the metal by the electrode. It is necessary not to lose sight of the length of the arc for a second. The size of the gas sphere, which prevents air from getting into the treated area, depends on it.
Important: although the work must be carried out quickly, it is impossible to make sharp movements by the electrode.
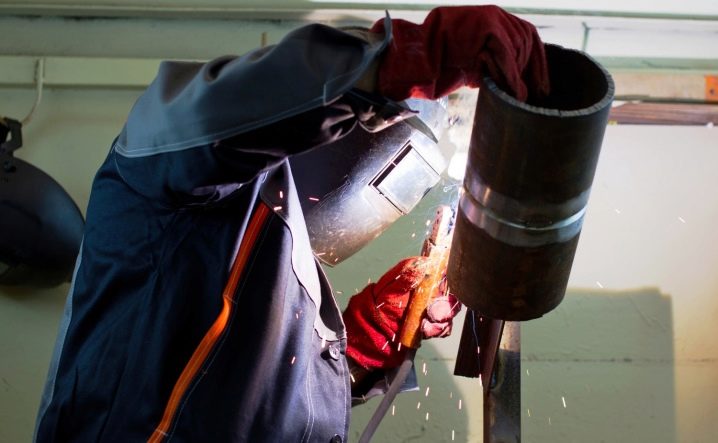
Any careless maneuver can disrupt the uniform distribution of the melting metal. In order to influence the thickness of the metal layer being deposited, it is necessary to carefully move the whole body either to one side or to the other. It depends on where the fusion should be. Working with pipes of large size, make seams inside and outside. This is especially important with a significant thickness of the metal.
Technological process
Work with reversal of the joint begins with the formation of tacks, after which two general seams are made. Now you can rotate the pipe 90 degrees and make the last seams, achieving tightness of the metal ligament. To eliminate burn-throughs, the first stroke is made with a 4 mm diameter electrode.
Optimal brands:
- WCC-1;
- CM-11;
- UONI-11/45.
The electric arc in this mode should have a current of 130 A (error - a maximum of 10 units). On the second and third layers, electrodes with a size of 5 or 6 mm are already taken, the current is increased to 200 and even up to 250 A. Otherwise welding of non-rotating joints is carried out. The need for it arises on the pipeline, which can not be moved. The initial layer is cooked from the bottom up, the subsequent ones - at the discretion of the welders - are sometimes performed in the opposite direction.
The most difficult to access places are boiled through a technical sidebar. When the connection of the parts closely adjacent to the cushions of concrete or to the walls of brick, is finished, the prepared hole must be brewed again. It is especially difficult to perform welding in the winter because the area being treated is rapidly cooling down. At the same time, the withdrawal of hot gases from it is complicated, which can make the pipe fragile; Only skilled professionals will be able to minimize this risk. It is equally important to avoid the occurrence of hot cracks and involuntary hardening of the metal. In this case, unlike metallurgical processing, it worsens the result.
Recommended:
- even more densely, than in a warm season, to join the connected details;
- warm the metal to a light red tone;
- increase current strength up to 20% against standard recommendations.
Such measures will help to create a completely viscous seam with normal ductility. Small wooden bars of a certain thickness help to level the welded pipes. In any case, arc welding of pipe joints is performed continuously, and the speed of movement of the electrode cannot be changed. It is undesirable to forget about your own safety, wearing protective masks and tight suits.
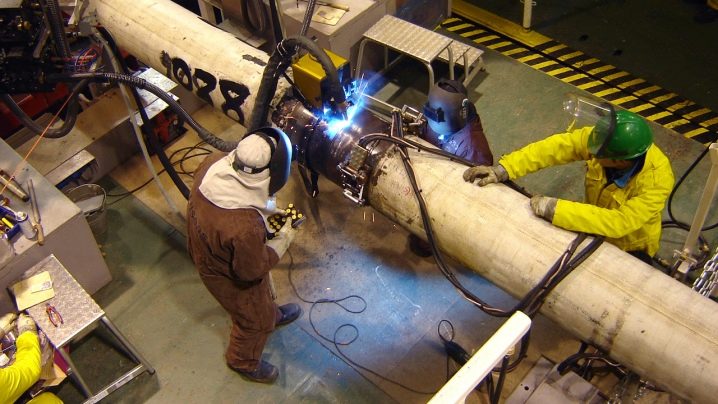
Swivel joints can be cooked as follows:
- conditionally break them into 4 segments;
- weld two, make a 180 degree turn of the joint;
- connect other segments;
- after turning by 90 degrees to form a second line;
- turn the pipe 180 degrees, then add the missing pair of parts.
Swivel joints of small diameter - up to 200 mm - are usually welded with a monolithic seam. In this case, the pipe itself rotates, and the division into segments does not apply. For your information: 2 and 3 lines go in opposite directions, and contiguous layers are made with a raid of 0.1-0.15 cm. Work with steel of increased strength also has its specifics. Only a specially selected thermal regime will help avoid the occurrence of quenching cracks inside martensite.
Very important and characteristics of welding materials. It depends on them whether the deposited layer of steel will be quite strong, whether it will not be weakened compared to the main part. Strengthened steel is welded both with heat treatment of joints and without it. Electrodes having a tensile strength of 600 MPa and higher are used. All of the above manipulations, we note, are carried out in the usual atmosphere.
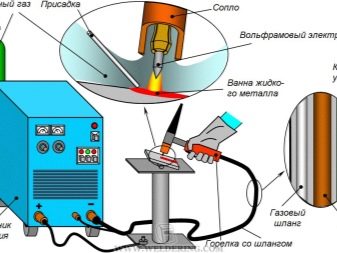
Inert gas treatment
Argon-arc welding of pipes, along with welding under the protection of helium, is necessary when obtaining thin pipe products with straight seams. The technology has been developed for structures with a diameter of 1.5-42.6 cm with a wall thickness of 0.02-0.5 cm.Argon arc welding can connect pipes made of steel with a significant amount of alloying additives. But in 60 seconds the welder will connect only 50-150 cm of the seam, which is much less than in other technologies. It is allowed to use the same systems as for welding by the radio frequency method or electrical resistance.
But the generator or transformer is replaced inside with a special apparatus. When working use not prone to melting electrodes. The edges of the blanks are not only melted, but also compressed under the action of the support rolls. If internal blowing is used, it is possible to reduce the size of unwanted elements. Since the walls are not thicker than 0.3 cm, and the welding pressure is high, it is not necessary to use filler material.
Argon as an insulating gas is good not only because of the steady arc, but also due to the reduction of metal sagging. In this sense, it is better for helium to work with stainless steels, with titanium. When it is necessary to boil pipes with a diameter of up to 10 cm, a tungsten electrode with an external cross section of 0.4 cm is required. For operation, constant electricity is used under voltage from 12 to 15 V and with a force of up to 200 A.By varying these indicators, you can choose the optimal mode for connecting pipes of a specific size.
For information on what technology is used to connect pipes by arc welding, see the following video.