How to choose and use pipe fittings correctly?
A fitting is one of the integral parts of a pipeline system. With it, you can redirect the highway in the desired direction or create its end. At the same time, the material used to make the fittings is very diverse: these are metal versions of the type of brass, steel, and polymeric compounds like polypropylene and polyethylene. His choice is determined by the material from which the main pipeline is made.
Also fittings are mounted using various types of connections: threaded, welded, flanged, etc. In order to fully understand the specifics of fitting products and the possibility of their correct application, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with all the details.
What it is?
A fitting is a product made of metal, polymer, or a combination thereof, necessary to connect several pipeline segments, ensuring its turns, pipe transitions to a different diameter, blocking the line with a dead-end plug, and also, if necessary, assembling and disassembling the hydraulic system from time to time.
At the same time, the main criterion for a fitting is tightness. A straight fitting is one that has all the holes of the same diameter, and a transitional one - which is different.
Kinds
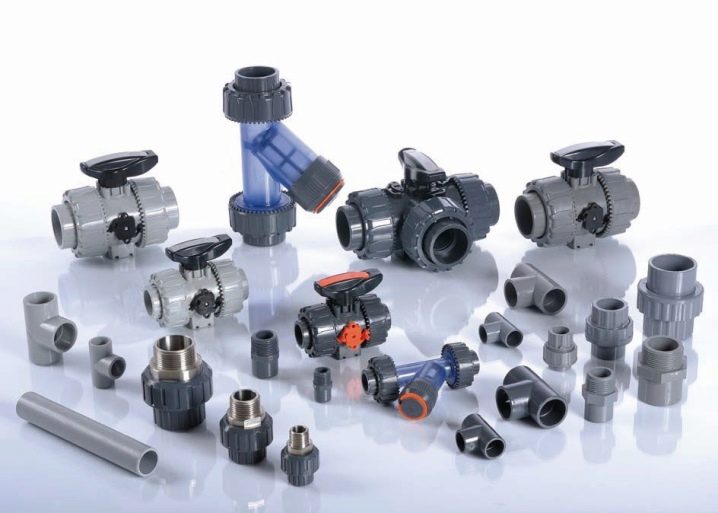
Fittings are classified according to several basic parameters. The most important is the material of manufacture, it determines the basic operational qualities. Also important is the type of connection and the shape of the product, which determines the purpose of the product.
Fitting connection happens with sliding and sliding elements. Use sanitary fixtures collet, cast of ferrous metals, etc.
According to the material manufacturing products are:
- Metallic: brass, copper, steel, cast iron.
- Polymer: polyethylene, polypropylene.
- Combined: metal-plastic.
For example, plumbing and soldering fittings made of PE are often used for swimming pools.
The main scope of brass fittings - brass and copper pipes. Most of the products of this material has a threaded connection, equipped with a compression ring to enhance its strength. The material is quite soft, so you need to tighten the thread without diligence, otherwise the probability of its damage and subsequent leakage is very high.
Copper fittings are suitable for connecting pipes from almost any material, except galvanized unalloyed steel. As a result of this contact, it undergoes chemical corrosion, leading to rapid deterioration of the pipe edges.
Products from copper differ in resistance to temperature differences and corrosion processes.
Products made of such material as cast iron are used for the manufacture of couplings, elbows, tees and crosses. The main type of connection for cast iron fittings is thread. They are not afraid of corrosion, they are very durable and have a low price, but have a relatively large weight. Cast iron has good pressure resistance, but this porous material can burst when subjected to water hammer. For this reason, it is not recommended to use such fittings in high pressure hydraulic systems.
Steel fittings have high strength and reliability, but are highly susceptible to corrosive processes. For a tight connection, threads must be sealed with tow or fum-tape. To connect the steel products can be used as a threaded and welded joint and other options that unifies their application. The most common steel fittings received when connecting several lines of different diameters.
The subspecies of stainless steel has a high resistance to corrosion, but its price is higher, which reduces the scope of economically feasible use. In addition, stainless steel products are susceptible to multiple assembly / disassembly without compromising structural integrity.
Polyethylene has high strength properties and durability, and in addition, low weight. It can be used in water mains and gas transmission systems. Fittings of any purpose and form are made of polyethylene: tees, plugs, sockets, bushings, etc. The fittings are equipped with both threads and are joined using liquid welding or hot boiling.
Polypropylene is widespread in the installation of hot and cold water. It differs in ease, simplicity in application, durability, lack of corrosion processes and easy installation. Polypropylene is used to create combined fittings that involve the transition from a metal pipe, for example, central water supply to internal polypropylene wiring. In this case, the metal tube can be connected by welding, and its shape oscillates between straight tubular and conical. The latter is a protective measure against the ingress of molten metal into and damage to the product in the polymer part, the deformation of the socket itself, as well as the narrowing of its diameter. In addition to plumbing, polypropylene is used in the sewage system and drain.
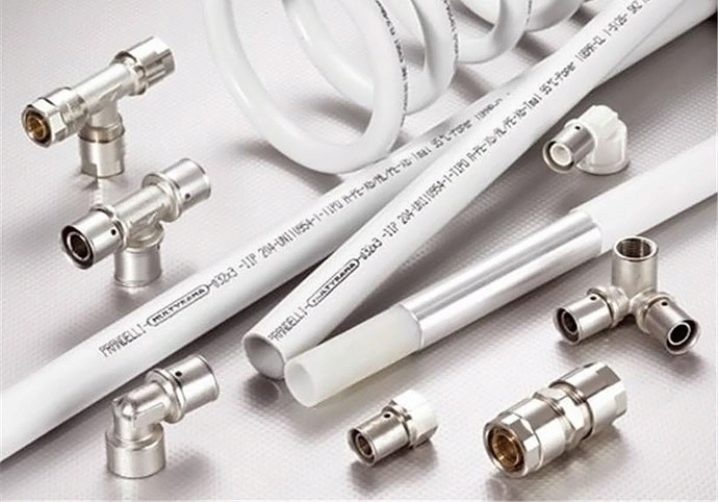
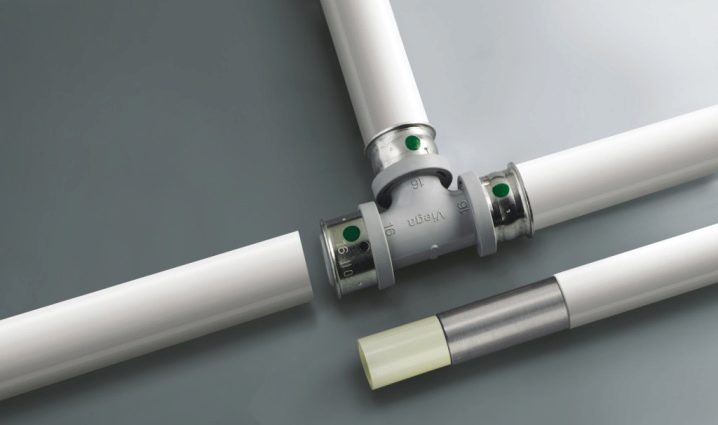
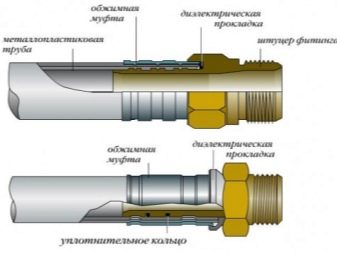
Metal-plastic allows you to create a combination of products that inherit the best quality from each of the materials. Fittings from metal-plastic are used in hot and cold water supply systems, heating, sewage systems, as well as the gas system, which requires high tightness inherent in metal-plastic fittings.
They are not afraid of temperature changes, and the plastic part protects the metal from corrosive processes. In addition, the elasticity of plastic compensates for the brittleness of the metal during hydraulic shocks.
Also products are easy to install and resistant to vibration and other movements.
To destination:
- turns;
- couplings connecting equal and different sized pipelines;
- crosses, tees, collectors;
- plugs and plugs;
- fittings connecting hoses of flexible materials.
By connection type:
- threaded;
- welded;
- flange;
- compression (crimp) - sealed with sealing rings and couplings;
- press fittings use special primers to create a seal;
- combined - combine two of the above types.
Threaded are used for the production of metal and polymer products. The installation of threaded fittings is relevant in water and gas transportation systems. They have a cylindrical screw thread. In terms of temperature, they can be used on pipelines with a maximum of about 175 degrees. The largest diameter of the connected pipes reaches 50 mm.The thread on the fitting is applied to the inner or outer surface, while the cutting length varies from the desired parameters of the joint.
The most popular in the chemical and petroleum industries, as well as the gas industry, are fittings made of alloyed stainless steel alloys, although the main area is still the water supply and heating systems for houses.
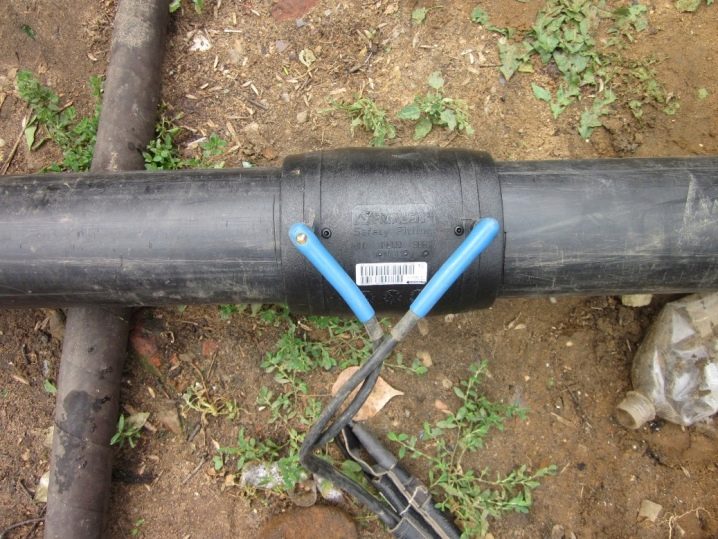
Welded fittings (they are segmented) belong to the category of non-separable (non-removable). They cannot be dismantled for reuse. The operating temperature for this type of fittings is the range from -70 to +450 degrees, and the pressure can reach 16 MPa. The ends of these products are smooth, which ensures an easy fit on the pipe and a further welding process.
At selection of a suitable fitting only the material of pipelines and dimensions of the joined sections are taken into account. The size range of welded nozzles is almost unlimited because of their widespread use, ranging from thin water pipes to massive pipes of gas mains.
Products are used for specificity, involving long-term use of the pipeline without replacing the docked parts of the structure.Because of the need for welding equipment and qualified specialists to work with them, welded fittings are used in places where the specificity of the pipeline places high demands on the connecting elements, in particular, on the operating pressure and temperature.
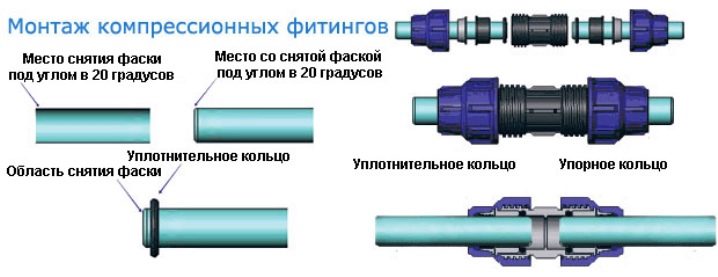
Compression (crimp) connections that use two compression rings made of elastic materials for sealing are mainly used for joining pipes of the same diameter. The technique is easy and quick installation with the ability to quickly disassemble the connection. It can be applied both to metal pipelines, and to highways from polymeric materials. The compression process is provided by a clamping nut on a tapered thread, which, as it moves to the narrow section, tightens the seal material more and more.
Installation of compression fitting is possible manually or with an automatic press. The technique allows deviation in alignment of the connected ends of the pipes within 3 percent. The strength of such a connection is lower than that of the welded or threaded type, the pipe can be pulled out of the joint under the influence of even manual force, since the ring of elastic material is not designed to operate at temperatures over 100 degrees.This type of fitting is not used on hot water mains, otherwise under the influence of high temperature rubber seal will become unusable and the tightness of the connection will be broken.
If one of the compression mechanism elements fails, the fittings are not repairable and must be replaced with new ones. They are most common in places with regular disassembly of the hydraulic system, for example, during irrigation works with a change of water source or lengthening the supply line.
Flanged fittings use special discs that are installed on both ends of the connected pipelines perpendicular to the section, and bolted together with the obligatory placement of the gasket, for example, rubber, graphite or paronit, to completely seal the joint. The power used to connect the bolts is determined by the operating pressure and the temperature of the pipeline according to GOST. Disks are most often fixed on the pipe by welding. A rarer option is to use a threaded joint.
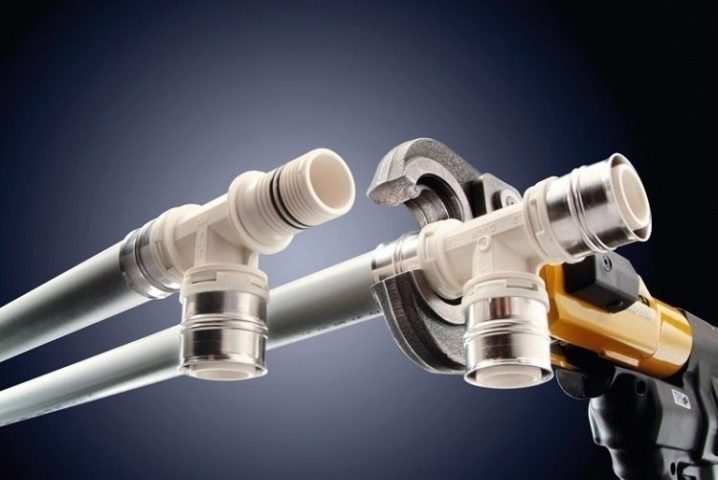
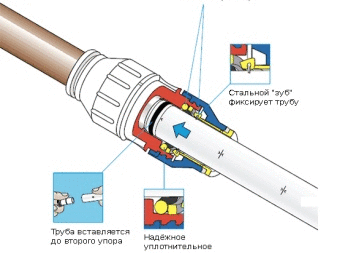
Press fittings are distinguished by convenience, installation speed and minimal installation hardware. The mechanism is as follows: there are several gaskets in the body of the fitting and two sleeves for sealing the pipes installed in it. The press-type connection is mainly used for linear connection of the line and allows you to quickly install a large number of pipes.
To install the fitting, you need special press tongs designed for working with product sleeves.
Also, fittings are equipped with antistatic rings to prevent electric shock generated by the difference in potentials of different materials used in the design of the fitting. It is also worth noting that their installation does not need a source of electricity, bulky gas-welding equipment, and the press tongs are designed in such a way that they do not require great physical strength. High reliability is ensured by the use of metal fitting joints. In addition, they are subject to disassembly by means of the same press tongs, but the fitting can be installed only in the same place, which requires drawing up a scheme of the pipeline and marking parts.
How to choose?
When choosing a fitting, it is necessary to take into account a number of factors in the order of their importance, namely:
- The material of manufacture. The best option is a fitting of the same material as the pipes to be connected.
- Dimensions of connected pipes. The inlet of the fitting must fully comply with the external diameter of the pipe. If different-sized pipelines are connected, a special fitting is required with appropriate inlet dimensions.
- Connection type. Both the required strength parameters of the joint and the means for connecting the fittings should be taken into account. It makes no sense to choose a welded type in the absence of a welding machine.
- Manufacturer. Externally, you can only establish the type of material, and its real quality, affecting the process of operation, can be checked only by experience. In this case, it is better to trust manufacturers with a good reputation.
- Appearance. A quality product should be smooth and smooth; there should be no sagging on its surface. If there is a joint in the design of the fitting, it must be even and neatly treated.
Recommendations for use
The thread is the easiest and most convenient way to install the fitting.
To do this, you need the following tools:
- gas wrench and adjustable wrench;
- screw die;
- sealing agent.
To enhance the tightness of the joint, connected by thread, in the pipelines for the supply of hot and cold water, flax soaked in red lead or fum-tape is used.
At a working temperature in excess of 100 degrees, the liner, saturated with graphite, bound with asbestos fibers acts as a sealer.
The installation itself is carried out as follows:
- the pipe is clamped by a clamp;
- in the absence of a thread, it must be cut, having previously processed the site of its location with linseed oil;
- then the material chosen to strengthen the sealing is wound onto the thread;
- on the opposite side the clutch is screwed all the way to the run;
- on the other hand, the treatment is similar to the first and is docked to the second side of the fitting, after which the coupling is screwed onto the end of the fit;
- using a pipe wrench, the coupling is tightened even more;
- further, it is necessary to test the tightness of the system by filling the pipeline with water;
- when a leak is detected, a locknut is tightened on its side;
- if this action did not help, the thread is twisted unevenly and it is necessary to reinstall it.
In the absence of a thread or if it is damaged or for another reason for which a threaded connection cannot be made, a coupling is used.
To install the compression fitting, do the following:
- the ends of the pipes to be joined are cleaned from agnails, the adjacent inner and outer surfaces of the pipe are also treated;
- the pipe is inserted into the fitting strictly in the center;
- a compression ring is put on the pipe;
- the crimp nut is installed and tightened until the joint is completely sealed;
- when tightening the nut, the force must be moderate, otherwise there is the possibility of thread breaking or breaking it.
How to choose a fitting for polypropylene pipes, see in the video.