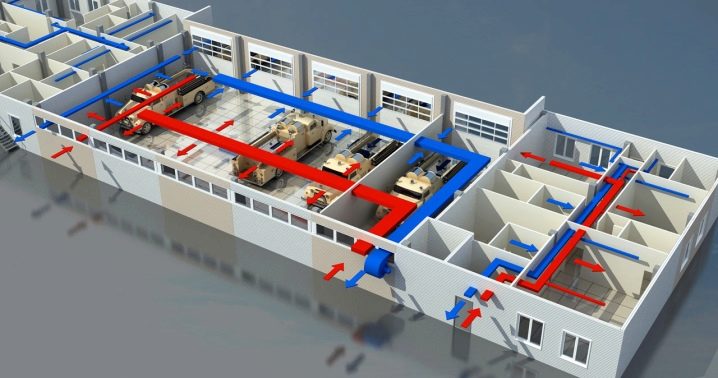
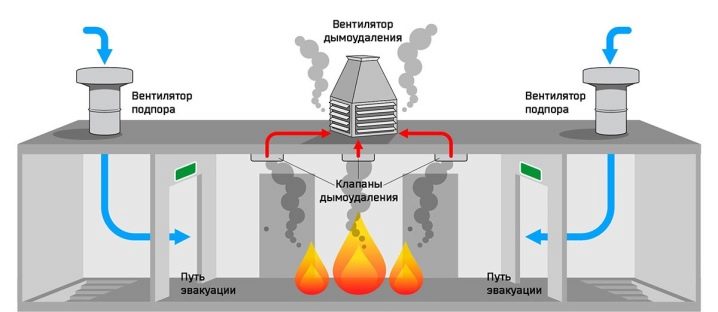
Basic design principles of ventilation

Ventilation is designed to provide a normal atmosphere and remove harmful substances outside the premises served. But it is not always possible to do it “just like that,” since it takes a lot of things to calculate and take into account. A competent project is very valuable, it allows you to exclude many errors and problems.
Special features
Ventilation designers deal with a “weightless” supposedly, but with a very capricious substance - air. If for the elaboration of the project of electrical wiring, plumbing and other communications, an increase in the volume of the building only increases the quantitative complexity of the work, then with ventilation it is not so.On an area of 1000 square meters. m arise qualitatively new problems. In addition, it is necessary from the very beginning to analyze where it is possible to use the natural course of air, and where it is necessary to help it. In some cases, the fans can not do.
Another caveat: you need to consider the location of the ventilation. If the building has one floor, this is one situation, and in multi-storey buildings the situation is different. Projects for such buildings as:
- residential buildings;
- production premises (with breakdown by industries);
- medical institutions;
- educational organizations;
- hotels and so on.
Design Standards
Consider exactly how to prepare projects of ventilation systems in all possible cases, it will not work. Therefore, it is important to focus on the general characteristic points. The principles are enshrined in the following three regulations:
- SNiP;
- sanitary and epidemiological standards;
- SanPiN.
Important: the ventilating systems of warehouse complexes and factory workshops are not subject to the building and sanitary rules that are needed for the design of residential premises.It is categorically impossible to confuse these regulations. Any project must meet the following requirements:
- clean air and microclimate;
- long operation of the ventilating and conditioning equipment;
- simplify the repair of these systems;
- limited noise and vibration activity (even for emergency ventilation);
- safety in fire, sanitary and explosive terms.
It is forbidden to provide in the projects all the materials and structures, as well as their combinations, which are not allowed for this type of buildings or for a specific area. All materials and parts that must be certified, are mentioned in the projects only together with an indication of information about the certificates. The minimum air intake per person in rooms and rooms with natural air flow should be from 30 cubic meters. For sites that are not ventilated through windows for any reason, this figure should be at least twice as high.
Normative documents
It is undoubtedly important to personally verify that the design materials meet the requirements.But it is necessary to go through approval in the supervisory authorities, although the need for such a procedure is not always. It can be discarded if only a reconstruction of an existing ventilation is carried out without a fundamental change in its parameters. Usually practiced coordination of all project documentation for the construction or repair in a single package. Separately submitting working materials for the design of ventilation for approval is required only when departing from general design solutions.
If a project is submitted for approval, it must have a strictly defined structure and a set of blocks. Their standard listing is as follows:
- title page, where the name is given, the initiator and performer are mentioned;
- the technical task in which the customer sets out everything that he considers necessary to implement, and also describes how to achieve this;
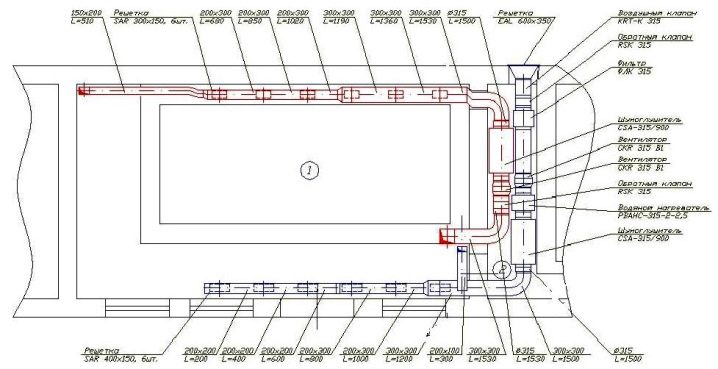
- a set of drawings in accordance with the requirements for design schemes;
- an explanatory material in which they write down which fans will be supplied, what the flow capacity will be and how many times they will achieve, how the control will be organized;
- a set of specifications for installed equipment;
- confirmation of coordination of the specified materials with designers and architects.
In addition to these materials, the explanatory block is complemented by calculations of a special kind. These include the calculation of the scale of heat losses attributable to the enclosing elements, and the calculation of the aerodynamic parameters of the ventilation complex. Only the structures listed in registered SROs have the right to compile all project materials. Thus, according to the law, constant mutual control of work efficiency is maintained. Now designers are required to use SP 60.13330.2012, as well as comply with all those standards, references to which are given in this document.
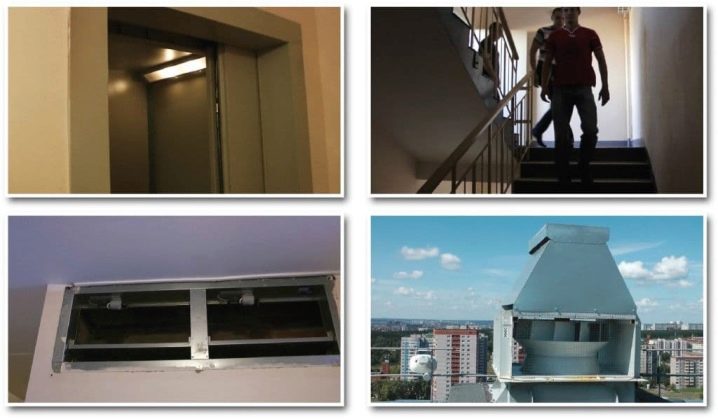
Regulations provide for a clear boundary between natural and forced ventilation. But regardless of the use of one or another option, it is required to ensure tracking of the smallest deviations of normalized indicators. According to official requirements, mechanical ventilation should be installed only where there is no possibility of naturally ensuring safety. So, special fans help to maintain normal temperature and humidity, if you can’t take them otherwise.According to the requirements of regulatory documents, it is also necessary to provide air pressure on the flight of stairs and inside the elevator shafts.
If these requirements are not met, the project will refuse to agree. When calculating natural ventilation, one should pay attention, first of all, to the difference in the densities of external and internal air. The air exchange rate should correspond to the conditions in a particular room. If in a residential house or in a wardrobe there is enough air renewal 2–3 times per hour, then in paint shops, at petrochemical plants, and so on, this figure should be 5–6 times higher. In any case, the regulations prescribe a balance when exchanging air: you can’t remove it more than pump it inside.
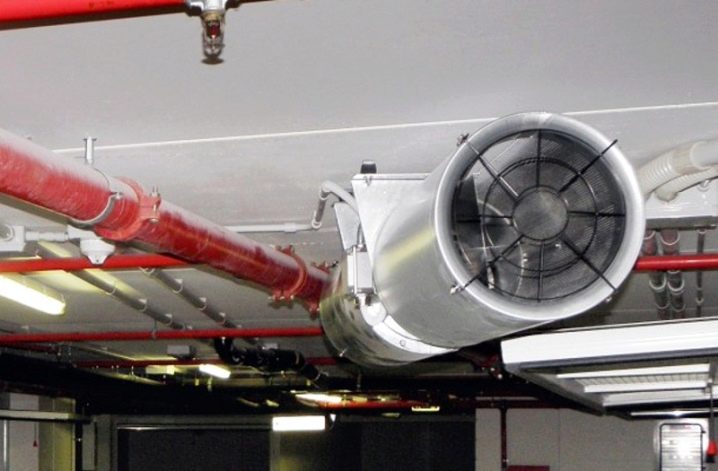
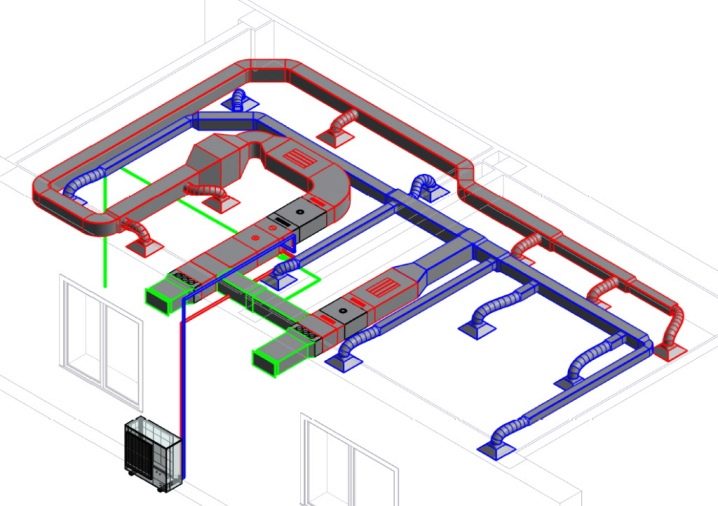
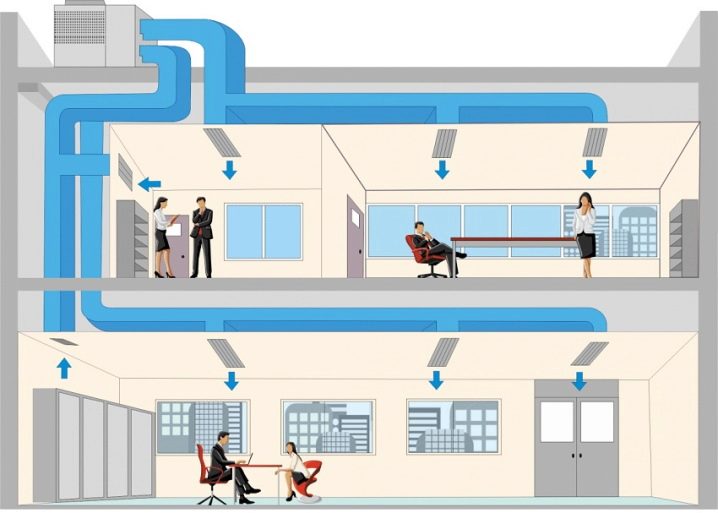
The common (sometimes referred to as general exchange - these are equivalent names) system is designed to provide air to the building as a whole. Local are those ventilation communications that are designed to supply air to individual zones or separate workplaces. It is strictly forbidden to pass general ventilation through a series of fire compartments. For any of them, it must be created separately.And it is also prohibited to merge in one branch of the complexes that provide recovery, and systems in which it is not provided.
Standards provide for the selection of power and the main characteristics of all components, taking into account the frequency of exchange of air, its losses. Additionally, pay attention to the natural pumping due to leaking walls. In the analysis of indicators pay attention only to the information that is reported by the enterprises that manufacture the equipment. It makes no sense to overpay for explosion-proof ventilation systems. All the same, they are not needed in residential premises.
Select the type of ventilation system
In addition to careful calculation of the parameters of the ventilating complex, it is necessary to pay attention to the selection of its type. To do this, pay attention to the following features:
- air pressure from the outside;
- need for inflow heating in winter;
- the required power of this heating;
- total need for admission and venting.
In turn, these parameters are selected according to the size, purpose, placement, workload of the serviced premises. The natural type of ventilation is simple, which attracts people in most cases.You can create it without the use of special equipment, so its failure is initially excluded. Even if the electricity is turned off, the system will freshen the air in the rooms or work rooms properly. But at the same time its performance is limited, and dependence on external conditions is too great.
The apparent flaws of the mechanical ventilation system for designers are not too significant, if only to take the matter seriously. Professional selection of key components minimizes the risk of breakage. And the number of options and flexible setting only positively affect the microclimate of the room. Having dealt with the natural or artificial method of work, you need to further make a choice what will be the ventilation:
- only ensure the flow of air from the outside;
- only throw out the polluted air;
- combine the performance of these two tasks.
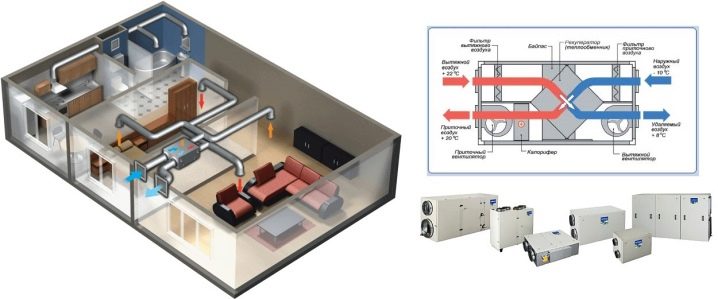
Hurry in making such a decision is not necessary. It is required to analyze a number of factors: how the room is planned, how many people use it, what danger of harmful substances, how large their intake, and so on.Both intake and combined ventilation systems in Russia can work normally only if there is an air preparation complex. The fact is that its temperature, humidity, chemical composition and other parameters with the direct collection of air outside are not always perfect. When all the specified parameters are determined, it is necessary to make another decision on how the ventilation system will be controlled.
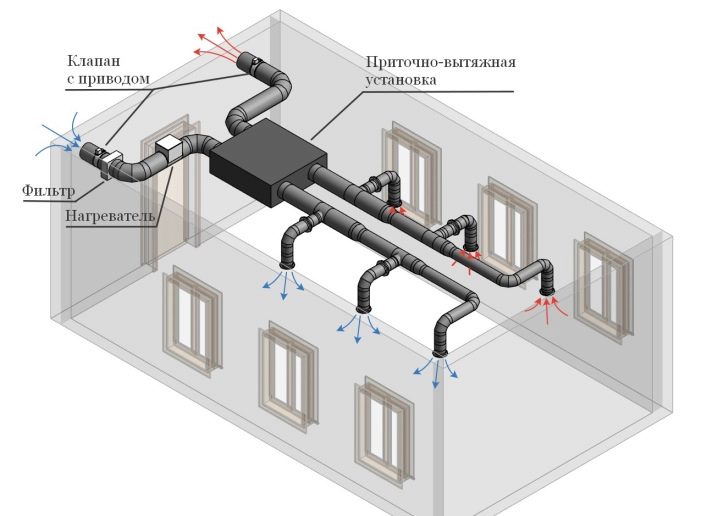
If there are no special wishes, and you just need to “make a good microclimate”, you need to dwell on a proven option - a supply and exhaust configuration. She will precisely cope with all tasks. An additional advantage is that the occurrence of pressure drops between the street and the house, between separate parts of the building is completely excluded. But complex cleaning systems need to be installed only at industrial and energy facilities. In residential buildings, if only the ecological situation is not close to catastrophic, you can do without them.
The main stages of design
Developers are very important to know this moment in order to better control the execution of their plan.At each stage of project preparation, it is almost inevitable that experienced specialists should assist. To select them, you need to look at the skill level, check the presence of state certificates and other evidence of the performer’s literacy. The executor should start by performing calculations that will show the required air exchange parameters in all parts of the object. Before this moment, selecting the main components, thinking through the schemes does not make any sense.
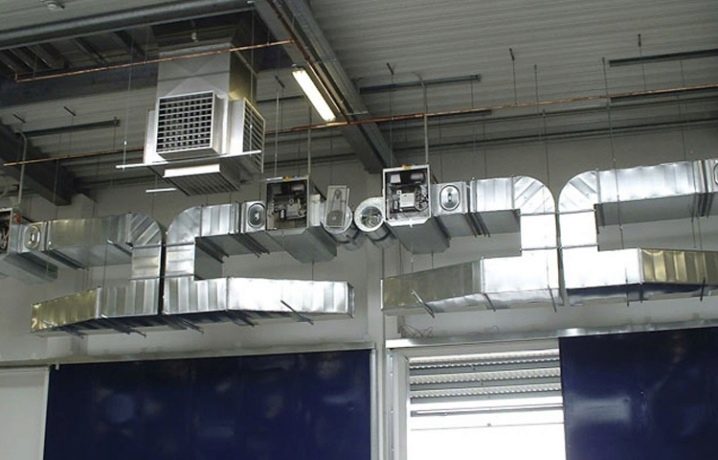
Having determined the key characteristics of future ventilation, the designers divide it conditionally into parts. Such a move helps to ensure the highest functionality and achieve security in the system. Separate fire-fighting apparatuses can be mounted in separate sectors. Additionally, when creating schemes, it is taken into account which dangerous situations may arise. At this stage, designers are required to consider how to avoid the entry of polluted air from one part of a house or an industrial building to another.
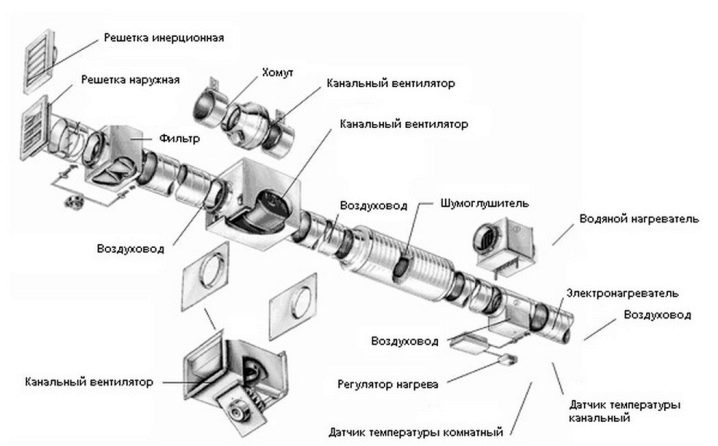
Only then proceed to the selection of technical means. Their characteristics are analyzed, taking into account the technical task and the previously identified specifics of the object, the conditions of its use.Next, it is the turn of the formation of three-dimensional models using modern software. Making sure that everything is done correctly, the model is transformed into a flat circuit. In this form, it becomes part of the package of documents submitted for inspection and registration with government agencies.
Air distribution
Ventilation must not be easy to inject a certain amount of air. Its purpose is to deliver this air directly to where it is needed. When planning the distribution of air masses, the following indicators are taken into account:
- daily mode of their use;
- annual cycle of use;
- heat input;
- accumulations of moisture and unwanted components.
Any room where people are constantly deserves the flow of fresh air. But if the building is used for public needs or for solving administrative tasks, approximately half of it can be sent to neighboring rooms and corridors. Where there is an increased concentration of moisture or a lot of heat is emitted, it is necessary to ventilate the areas of water condensation on the enclosing elements.It is unacceptable to move air masses from areas with increased pollution to places with a less polluted atmosphere. Temperature, speed and direction of air movement should not contribute to the appearance of a foggy effect, condensation of water.
Calculations
Competent calculation of forced-air ventilation implies the definition of its parameters:
- total air flow;
- normal system pressure;
- heating power;
- cross-sectional area;
- the size of the inlet and outlet;
- electrical energy consumption (for mechanical systems).
Performance is calculated on the basis of data on the height and area of the premises, on the use of each site and on its workload. When choosing the multiplicity of passage of air through the ventilation, it is impossible to deviate from the values prescribed by the SNiP. If necessary, only amendments are introduced for the heating characteristics and for the number of people present. For most residential apartments, 100–500 cu. m of air in 60 minutes. And if the area of the apartment is large (or you need to ventilate a private house), this figure will be already 1-2 thousand cubic meters. m
Review the design of ventilation systems, see the following video.