Choosing a frame for the greenhouse
Gardening often grows from a common hobby into a business that starts to make a profit. In order to grow fruits and vegetables in a cold spring and not too long summer, it is necessary to equip a greenhouse on the site. It can be of any shape and size, made of a huge variety of materials, but any greenhouse is going, first of all, from the frame.
Special features
The frame is a supporting structure on which a light transmitting coating is mounted: polycarbonate, film or glass. The choice of material for the frame should be approached responsibly, since a certain number of tasks are assigned to the frame. The frame, to which the translucent coating is attached, not only determines the shape of the greenhouse itself, but also maintains a certain temperature inside, while resisting the influence of weather conditions.And most importantly, the frame should be easy to assemble and lightweight material.
Materials
In order to determine the material of the frame, it is necessary to consider the main types of greenhouses, depending on the type of structure and shape of the shelter. There are two main types of greenhouses - summer and winter. The latter differs from the first more robust design, the presence of the foundation and the heating system. It is obvious that the construction of a small winter greenhouse in the country or near a private house will be much more expensive than installing even a fairly large summer greenhouse.
The shape of the coating greenhouses can be divided into the following types:
- gable "house" or a single-wall near-wall greenhouse;
- spherical, domed or arched;
- trapezoidal;
- polygonal greenhouse of the difficult form.
To determine the material of the frame, you must also determine the material of the coating. One of the most common is polyethylene film. The cheapness of the material allows to annually cover the greenhouse with a new film, maintaining the required temperature inside the structure. If there are additional components in polyethylene,You can improve heat retention and increase sunlight penetration.
For the construction of summer greenhouses reinforced polyethylene film is in the greatest demand.which is stronger than usual. For all its merits, the film is a very fragile material with a short lifespan. It creates the effect of a “membrane”, due to which condensate accumulates on the inside and which prevents the free circulation of air in the greenhouse.
The second variant of the material may be glass, which transmits light best and has high thermal insulation. Fruits and vegetables are protected by glass from dew, rain and other precipitation. The disadvantages of glass are its high cost, brittleness and a big demon, as a result of which there are difficulties when glazing a greenhouse.
To date, cellular polycarbonate replaces a cheap film and expensive glass, despite the fact that he, too, is a very expensive material. It is produced in the form of large sheets 4-32 mm thick. Polycarbonate has excellent transparency, high thermal insulation performance and low weight. It is easy to bend and assemble without compromising breaking.However, it can be deformed when temperature drops. Polycarbonate over time loses its high transparency and must be completely replaced.
The most common materials for greenhouse cover include spunbond and agrofibre. Such materials are made of polymer fibers and most of all resemble a fabric of white and black.
A warm garden on the site can be equipped with your own hands or ordered to be erected from professionals, but, in any case, three types of material can be used to frame all types of greenhouses: wood, plastic and metal.
Tree
Wood is the most popular material for building a greenhouse. Working with a tree requires a minimum of tools and basic skills to work with them. This is the cheapest frame material with which you can use all types of coating, but it has several significant drawbacks.
Wood is more prone to rotting than other materials., especially in contact with the soil, so the wooden base will stand for about 4 years. Also from it it is impossible to equip a winter greenhouse. Treatment with anti-fungal agents does not help much, therefore, to increase the service life of the wood, the framework can be placed in metal pipes.The second disadvantage is that the wooden timber does not bend, therefore it is impossible to make a rounded roof or walls of the greenhouse. When covering hard corners of such a frame with cellular polycarbonate, many small cracks are formed, which have to be sealed.
Plastic
Most often, frames for greenhouses are made of PVC pipes, which are perfectly bent, easily glued to each other or are put together with ordinary scotch tape. Plastic is a low-cost material with low thermal conductivity, it is easy to replace its deformed part with a new one, without dismantling the entire frame. However, he, like the tree, is not suitable for the construction of a winter greenhouse, because it is quickly covered with cracks from low temperatures and is not attached to the concrete foundation. Plastic can not be used in conjunction with a polycarbonate coating, since the latter is much tougher than the frame itself. In general, the construction of PVC pipes is very unreliable and can be deformed even by gusts of strong wind.
Metal
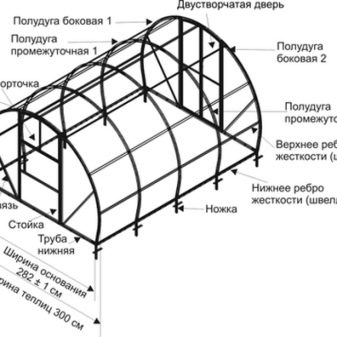
The iron frame is the best solution for creating a large winter greenhouse from available materials. Particular attention should be paid to the construction of the foundation, as the frame structures made of metal have considerable weight.The material most often used are shaped tubes, aluminum or zinc coated profiles.
Aluminum profiles do not need to be painted, they are tough enough to use polycarbonate as a coating, but lightweight and last a very long time. Among the shortcomings can be noted the high cost of the material and the complexity of a hand-made installation. Buying ready-made kits for the construction of greenhouses limits the size and shape of those options that are presented on the market of construction services and materials. When assembling by hand, it also becomes difficult to buy a certain number of profiles that are sold in large bulk.
Profiles for drywall are just galvanized and they can also be used for the construction of a warm garden in the country or behind the house. Of these, you can make rectangular and polygonal greenhouses, but it is impossible to build arched or spherical, as galvanized profile practically does not bend. At a low price, they are strong enough, weigh little and serve for a long time. The most important thing is that it is necessary to carefully cover such a framework, since sharp joints in the profile can damage a thin film or carbonate.
From a profile pipe it is easy to weld a framework for the big stationary winter greenhouse. Sturdy pipes are easy to attach to concrete, keep the shape of a bend and almost never collapse with time. High thermal conductivity can be reduced by painting the metal with a light color and coating with cellular polycarbonate. It is very important to have the skill of bending the profile pipes on special equipment or manually, so that the frame is sufficiently smooth and stable. In the absence of such a skill, the frame can be all-welded and acquired already in finished form.
Drawings and diagrams
After selecting the structure and material, the drawing up stage begins. If you do not have a special graph paper on hand, you can use ordinary tetrad sheets in a cage, it is also quite convenient to arrange the elements of the drawing on them. All the construction of the project should be carried out with a simple pencil, since it is easier to erase it in case of an error in the calculations. If you have design experience, you can also use a special drawing program, for example, Compass or Autodesk AutoCAD.
It is necessary to make a plan in at least two forms - from the long side of the wall and from the end.Also an excellent idea of the finished greenhouse will give her project in isometric.
Design is carried out in stages.
- Scale definition. To do this, you need to take the planned size of the greenhouse and translate them into a ratio so that the picture fits on a small sheet. For example, when choosing a large square greenhouse with dimensions of 6x6 meters, you can draw a square with a side of 20 cm, then the scale of the drawing will be 1: 30.
- Drawing of the external contours of the greenhouse with a given length, width and height.
- The foundation or base of the greenhouse is determined and applied depending on the chosen construction.
- Drawn wall supports. In the case of designing a single or dual roof, the roof system is also drawn at this stage.
- Various horizontal elements and openings are added to the drawing - lintels, windows and doors.
- Final detailing is carried out and various notes are put on the finished design, type of material and fasteners. For example, you can specify that a 20x20 or 25x25 mm thick profile will be used for the construction of the greenhouse, the coating will be polycarbonate, and the polycarbonate will be fixed to the frame with a self-tapping screw and washer.
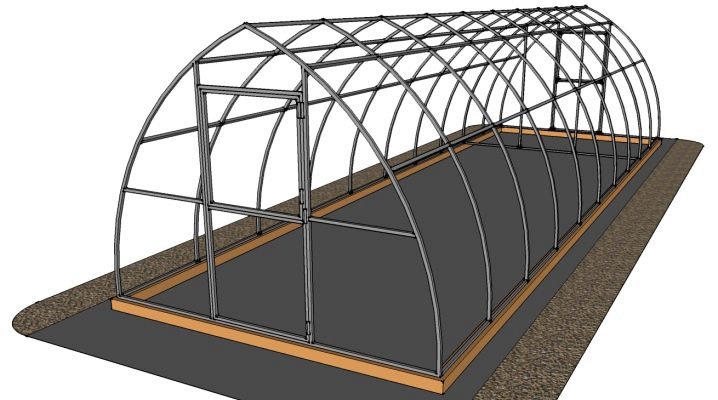
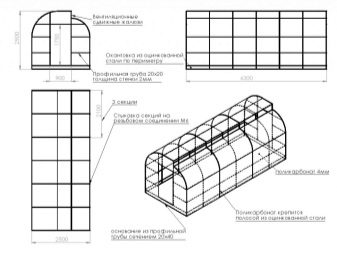
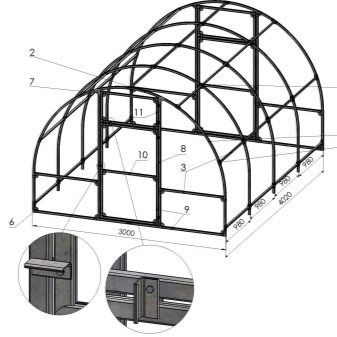
Each type of greenhouses has its own design features.For example, the height of an arched greenhouse usually does not exceed the height of a bent polycarbonate sheet. Depending on its standard height, the roof of such a greenhouse will be at a level from 1.9 to 2.1 meters. Since an arched greenhouse requires a curved frame, to construct a drawing, it will be necessary to calculate the bend radius. Such a radius should not exceed the maximum allowable bending radius of polycarbonate sheets specified by the manufacturer.
For a greenhouse up to 3-4 meters long, you can use only two arcs on the ends as vertical supports. If the length of the greenhouse is more than 4 meters, it is necessary to add additional supports at a distance of 1-1.5 meters from each other. Such arcs are attached to a rectangular metal base of the greenhouse and horizontal guides between themselves.
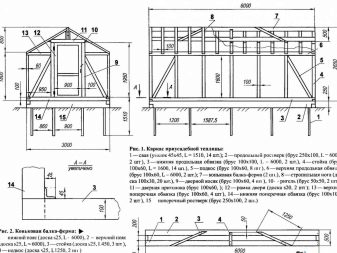
For a single or gable greenhouse it is necessary to choose the correct angle of the roof - it should not be less than 20 degrees and not more than 45. For the framework, it is desirable to use a durable steel profile, and to ensure strength between the vertical and horizontal elements add additional diagonal braces.For convenience of calculating the size of such a greenhouse, one can proceed from the length and width of a standard polycarbonate sheet. Then there will be no need to cut a sufficiently strong material in width or length to cover the area of the required size.
Dome greenhouse (geocupol) is the most difficult type of greenhouse, but also the best in terms of illumination and resistance to strong wind and snow. Such a structure is created by connecting a large number of hexagons or triangles into a single system. It is easier, of course, to build a greenhouse with triangular elements. A stable geocupal can be erected of almost any size, but the most optimal is a diameter of 4 m and a height of about 2 meters. With such dimensions, it will take about 35 triangular elements with an edge length of 1.23 m and about 30 pieces with a length of 1.09 m. In order to calculate the exact number, you can use a special calculator.
Installation details
Before you start directly mounting the frame with your own hands, you need to start in advance to prepare all the materials and tools. To purchase in the hardware store fasteners, plumb, metal shears or saw and shuropovert.
After that, you can proceed to the process of construction.
- The platform is cleared and leveled in the place where the installation of the frame is planned. It is also necessary to thoroughly clean the place of weeds and grass, as in greenhouse conditions they will grow and displace cultivated plants.
- The marking on the area is made and the foundation is equipped, if necessary. To build it, you need to remove the top layer of the sod and set up a double-circuit marking with pegs and a cord. Then a trench of the required size is dug, depending on the greenhouse design chosen and the frame material used. The finished trench is lined with a special membrane for protection against moisture and is poured with a mixture of sand and gravel cement. To strengthen the foundation, you can additionally insert metal pegs along the perimeter of the trench or even assemble a separate frame from them.
- The assembly itself is carried out either directly on the prepared site, or close to it, in order to make it easier to transfer the finished wreck to the right place.
- We divide the timber or profile into pieces of the required length in accordance with the drawing. Wood is sawn, metal is cut with special scissors, plastic is broken off or cut with a knife.When building an arched greenhouse, the profile is bent at the desired angle manually or with the help of special equipment.
- The first is going to base. Wood is connected with screws, plastic is glued, and metal can be welded with a special apparatus.
- Then, the end parts are assembled immediately with the doorways and are attached to the finished base.
- If necessary, additional vertical supports, horizontal and diagonal guides are assembled and fastened.
- The finished frame is installed on the foundation or simply transferred and fixed in the intended place. After that, you can proceed to the trimming or glazing of the finished structure.
Before stretching the material, the frame can be painted or treated with various solutions against rotting or corrosion.
Tips
When assembling an aluminum frame, it is better to buy perforated corners, this will significantly simplify the assembly and coating of the greenhouse. The design of the summer greenhouse can be made collapsible, then its service life will be significantly extended due to storage in a warm dry room the entire autumn-winter period. If the greenhouse does not understand, then it is necessary to clear snow from it in time in order to eliminate the risk of deformation and the breach of the roof.
If the greenhouse is located away from a permanent place of residence, in a country house outside the city, the snow is not always cleaned in a timely manner. In this case, it is necessary to build a reinforced structure, which is selected depending on the weather conditions of the region. Such greenhouses, as a rule, have a metal frame more than 1.2 mm thick. An additional thin arc welded from below to the main arc can act as an amplifier of the arches of a greenhouse. Additional transverse or longitudinal lintels can be positioned in the upper part of the gable wooden greenhouse. And also it is possible to reduce the distance between the vertical and horizontal elements of the frame, which also reliably strengthen the structure.
The transparency of polycarbonate is affected by the thickness of its sheet. Polycarbonate with a 4 mm cross-sectional sheet would be better to let the sun's rays than polycarbonate with a 8-mm cross-section sheet. However, the latter is much stronger and less prone to deformation when heated and cooled ambient air.
The least frequently encountered type of greenhouse is a recessed greenhouse. In this case, above the surface is only its roof, and the rest of the space is located underground.For the summer period, the roof of such a greenhouse is removed and seedlings are grown in it.
You can experiment with a non-standard form or choice of material for the greenhouse, make it a small collapsible design or build a real glazed greenhouse. The main thing, having studied all the advantages and disadvantages, is to choose carefully and be able to assemble such a greenhouse on your own.
How to choose a frame for the greenhouse, see the following video.