How to make a greenhouse in the country?
In order to harvest a large crop of pepper, it is necessary to know how to ensure optimal conditions for its growth. Experienced gardeners know how to make a homemade greenhouse with their own hands. They are well aware of which types of greenhouses are suitable for a particular plant variety, which materials are better and more profitable to use for arranging structures that protect the soil and seedlings.
Purpose
Garden owners, by definition, are well aware of the purpose for which soil protection structures are used.
It should start with clarification. Not everyone knows how a greenhouse differs from a greenhouse. Consider the examples of the nuances of the structure of these structures. Let us determine which tasks are solved by the specificity of these structures.
What is different greenhouse and greenhouse?
Greenhouse and greenhouse - similar facilities designed to protect, planted in the ground. To clearly understand the difference, we define what the protection of the soil.The subject literature says that in order to protect the soil on which various plants are grown, special structures are used to ensure the process of natural or technical heating.
These designs include the products described below.
- Greenhouses with a frame of wooden and metal parts, with glazing or film as a covering material.
- Greenhouses, made in the form of pits with strapping, or bases, covered with window frames with glass or PVC film.
- Frame construction, the carrier of which consists of wire or plastic, covered with films.
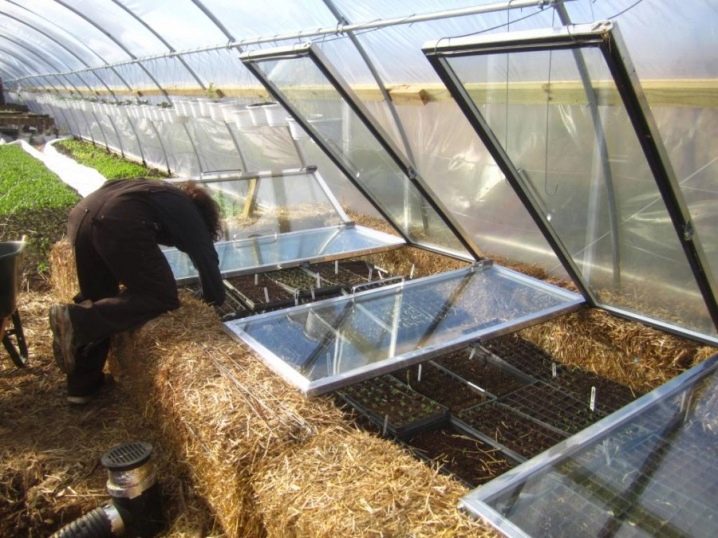
- Frameless modifications in the form of frames, closed film. These special structures perform a protective role for the soil and the seedlings planted in it. In all cases, protection is provided by a covering material, which can be used as a cheap non-woven fabric, polymer film, polycarbonate or glass.
Kinds
Greenhouses share:
- on terms of service (in winter, spring, summer, autumn);
- by type of supporting structures (without frame, frame, multi-span);
- by specialization (cultivation of vegetables, sprouts seedlings);
- on covering material;
- in shape (vertical / sloping walls, sloping / gable, etc.).
Individual characteristics due to local requirements may vary significantly. Constructions may look like small greenhouses in the garden, or in the budget version as a crest covered with film. The main task is to make plants feel like at home.
Of particular interest to the domestic buyer are modern budget solutions - the greenhouse "snail" (portable version) and the small greenhouse "lotus". Understand their installation is not difficult, even far from the technology person. The instruction included in the kit explains in detail and step by step all the nuances.
Portable "Snail" can be installed on any site. The design will perform the stated functions even when installed on the ground without a prepared foundation. It is possible to rotate the mini-greenhouse along the beds, for alternately growing seedlings in different parts of the garden. Installation of the facility will not take more than an hour, which is a significant bonus.
A competent gardener begins with the cultivation of greenery and vegetables, for which protection is enough greenhouse.Its dimensions are substantially less than the greenhouse, which does not make its protective properties worse. The supporting structure of the greenhouse "Lotos" is made of pipes coated with zinc.
Coating is cellular polycarbonate. Unlike short-lived film, polycarbonate will last more than one season. It is easy to maintain, provides maximum illumination for plants. The airing of the structure is carried out with the help of two leaves (like lotus petals).
The opening, which opens with a light movement, provides the necessary flow of fresh air.
Materials
Installation of any type of product begins with the construction of the supporting structure. Consider the typical types of materials that make the frame for greenhouses.
Dougie
It is not in vain that arched greenhouses are respected both by experienced gardeners and beginners. It is difficult to overestimate the simplicity and speed of installation of this design during sudden frosts. Its dismantling is also easy and simple, does not require special skills and special efforts.
The main components of the structure are arcuate elements that can be made in an artisanal way.
To discuss the properties of a particular material is quite difficult.In certain conditions, disadvantages can be an advantage. Consider the main characteristics that necessary for the effective functioning of the structure:
- Strength. Arcs must withstand bending stress, rain and snow. They must also resist deformation of the coating material.
- Ease of care. The less attention is required from the gardener, the more time he will be able to devote to the garden plot.
- Low weight. This feature is especially important when alternately growing seedlings in different parts of the garden.
- Good flexibility. Gone are the days when making arcs did not do without a pipe bender. This property is important for many factors. It affects the stability of the shape of the greenhouse, its rigidity.
- Fortress and durability.
Arcs are made:
- from metals (with various coatings);
- from plastic;
- from improvised material (wood, planks, twigs of willow, wire, fiberglass reinforcement).
Profile pipe frame
Usually a metal profile tube is used when installing greenhouses with polycarbonate coating. Obvious advantages:
- special strength allows you to easily withstand the weight of the plastic coating, to counteract the climatic influences (snow loads);
- rigidity metal frame made of steel pipe allows you to easily attach additional equipment (irrigation, lighting and heating systems).
Among the shortcomings can be noted the inflated prices for the material and its tendency to corrosion.
Framework from PND (polypropylene pipes)
Consider the pros and cons of this material.
Advantages:
- environmental friendliness;
- flexibility;
- ease.
Disadvantages:
- limited temperature conditions of operation (fragility at -15 degrees);
- deformation under the action of ultraviolet.
Metal frame
Pros:
- anticorrosion (aluminum and galvanized profile);
- strength;
- design variability;
- installation on the foundation;
- efficiency in the winter;
- transparency (large openings);
- long service life;
- universality (all climatic zones).
There are a few minor drawbacks - high prices and not very reliable methods of fasteners.
Frame made of metal pipes
The basis of this design is an aluminum base, covered with a shell (polyethylene).Glued polymer layers protect the metal core. These components have sufficient flexibility to provide the necessary functionality of the structure.
Covering materials
Differ in structure on hard and soft.
The first type includes glass and different types of polycarbonate. To the second - PVC films, reinforced films, non-woven material.
Until now, the most popular covering material is polyethylene film. The source of this popularity is the optimal ratio of quality and price.
Technologies are rapidly developing and thanks to them the characteristics of materials that are well-known are improved. Modern films have:
- hydrophilic qualities (their surface does not allow condensate to accumulate);
- heat saving;
- UV resistant;
- antistatic ability - the film does not attract dust, increasing the light transmission feature;
- increased strength (reinforced film);
- ability to stretch (stretch).
However, the flaws are also traced - such a film is weakly opposed to shocks and cuts, and also quickly becomes unusable.
Agrofibre
Unlike films, this material is more durable. Wear resistance is achieved due to polymer fibers. Differs in ease and ability to pass a moisture, but does not keep enough heat.
Glass
Everyone knows the glass shine of greenhouses, especially industrial greenhouse complexes. The absolute light transmission capacity of glass is unparalleled.
The main disadvantages are fragility and large mass.
Spunbond
The most popular covers for greenhouses are made of spunbond. Consists of polymer fibers. It is considered the best covering material. Nevertheless, after each season, it is necessary to carry out disinfection - spunbond accumulates fungi and all sorts of viruses well.
Making homemade designs
After reviewing the key points and the main characteristics of materials to protect the soil, let us consider an example of the process of building a country homemade greenhouse for pepper. What is different from the greenhouse greenhouse, so it is that it does not provide heating. To make the greenhouse convenient to use, it is necessary to think over all the technical aspects in advance.
Pepper protection must meet the following requirements:
- have sufficient lighting;
- provide full access for regular watering;
- be well ventilated (to avoid overwetting);
- keep warm
To ensure the most comfortable growing conditions for pepper, you need a lot of light and heat. In order to as a result of installation work turned out functional construction to protect the soil and plants, you must:
- determine the place;
- make a list of materials;
- consider the steps for installing the basic structure;
- select coverage.
The choice of location is determined by:
- light;
- smooth surface (without bevels and ditches);
- optimal distance from trees and buildings;
- orientation of buildings from east to west;
- dry area without waterlogging.
Site preparation
It is recommended to install a greenhouse under the pepper on a warm warm soil, which can provide normal conditions for the functioning of the root system of plants.
Deepen the selected area to a depth of half a meter, align the bottom layer of the pit. It is recommended to remove all old roots from the ground.
We make a homogeneous mass from straw, clay and water.Fill the groove halfway up with this mixture, wait for it to dry. Prepare humus - mix dry leaves, scraps of paper, bird droppings. Pour the mixture on the dried mud solution and ignite it. The recess, heated by burnt humus, can be covered with slate, for more heating of the earth. After the end of smoldering, the ash is evenly distributed over the area of the depression. Top piled fertile layer of peat, sand, manure and black soil.
The main factors determining the choice of materials are financial capabilities and local conditions. The modern range provides high-quality products for greenhouses of any range of cost and complexity. Traditionally, for peppers are considered optimal:
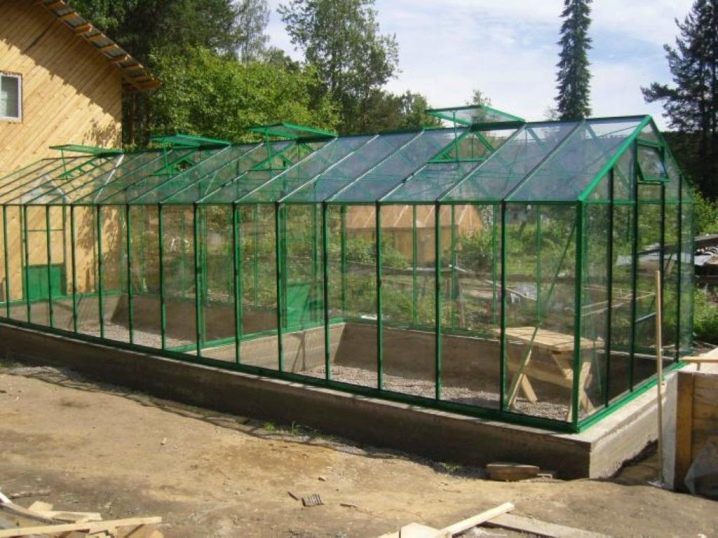
- polycarbonate greenhouse;
- glass construction;
- construction under the film.
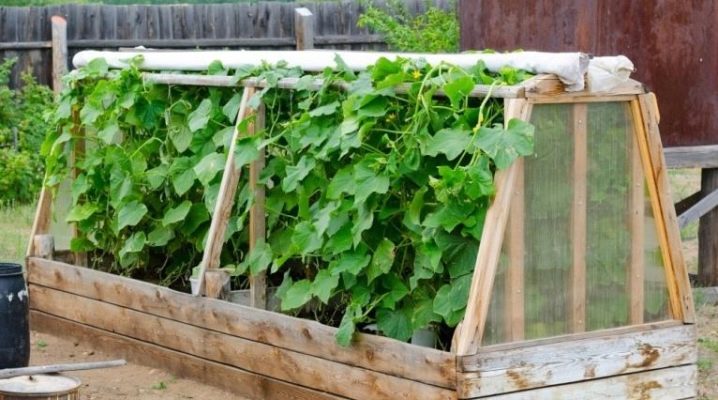
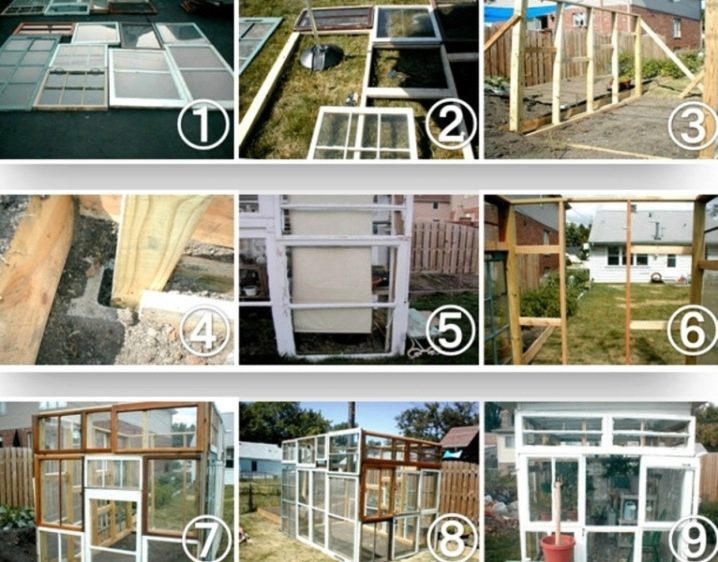
The old window can play the role of a budget option greenhouse design. For example, a wooden greenhouse with a folding frame is the most mobile way to protect seedlings. It is easy to move around the site, it is strong and durable. This is an example of how you can quickly make a greenhouse to give your own hands. It will be cheap and reliable.
Analogs of this design are suitable for the protection of strawberry and eggplant seedlings. If necessary, you can make collapsible frame. For the basis of the trim trim will fit. The simplicity of the building allows you to use for its construction the remnants of a wooden profile, drywall, old window (frame) to make a comfortable sash.
Drawing Preparation
Usually at this stage, the layout, structure of the greenhouse, its dimensions are already taking shape. After checking with the consumables, it remains to make a simple drawing. As a rule, this procedure is not difficult. Otherwise, you can take the finished drawing and substitute in it its size. The scheme should be well thought out and contain a maximum of visual information.
Equipment and tools
The device of the greenhouse in our case involves working with a wooden structure, so we will need following tools and accessories:
- hammer;
- screws (for individual situations nails);
- corners (of metal) of various sizes;
- hinges;
- screwdriver;
- boards (of various sizes), bead (slats);
- arc (PVC pipe);
- coating (polycarbonate or film);
- staples;
- level (tool).
Before assembly, the finished wooden parts of the construction are treated with antiseptic compounds in order to avoid the appearance of pathogenic microbes in the future.
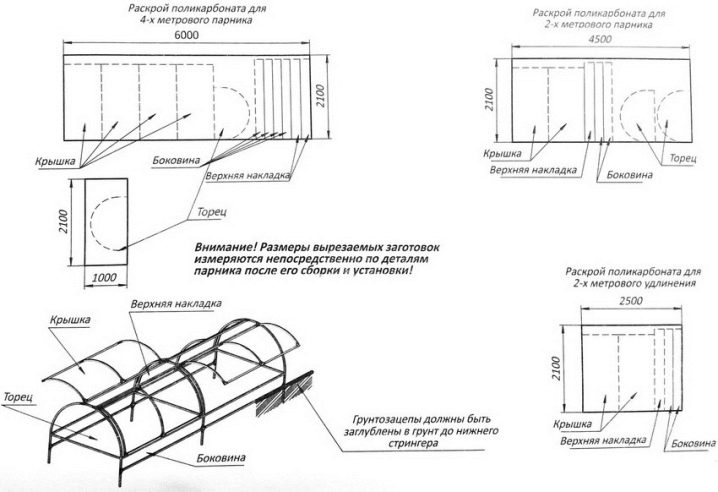
One of the determining factors when choosing a covering covering is the size of the greenhouse. With small dimensions can be limited to the film, in other cases it is recommended polycarbonate. It is better to start cutting after the installation of the frame.
Assembly and installation
The main types of structures:
- from old frames;
- arched;
- on the foundation;
- with walls;
- frame.
The most common design and cost-effective solution - the greenhouse of the old window frames.
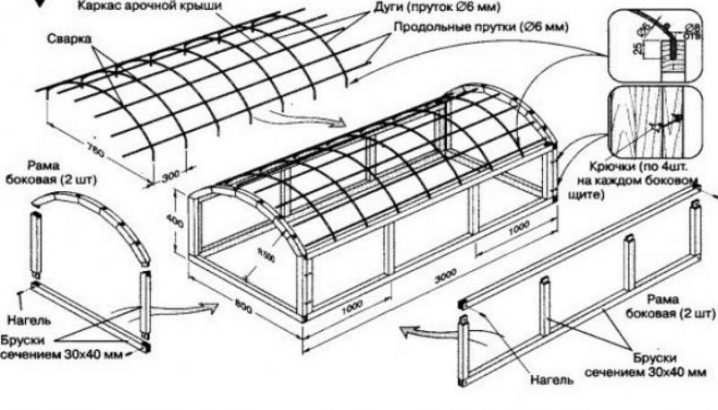
To properly build a greenhouse, you should observe the sequence of operations. First you need to install the box of our greenhouse on the foundation. A good option would be to make a cleaned, rammed, flat place. The work needed for this is done with the help of a building level and strung ropes. At the right angle do the foundation (timber or brick). The boards of the box are fastened with nails or self-tapping screws, it is recommended to fill the seams with sealant.
Fitted to the size of the old window frames should be slightly wider than the box to provide reliable protection from heavy rain.If the frame is covered with a film, the places of its attachment with the help of rails are carefully treated with a sealant. The junction of the box and the frame is located on the north side, with the calculation allowing full opening of the frame.
Making a greenhouse can be a different device, for example, if plastic pipes are laid on top of the box, which should be pre-cut and bent. The construction of the greenhouse can be considered complete after fixing the covering material.
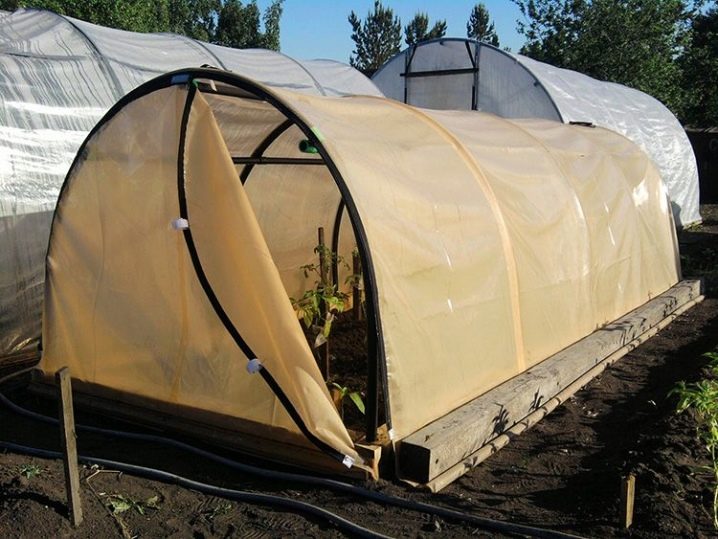
Arc structure
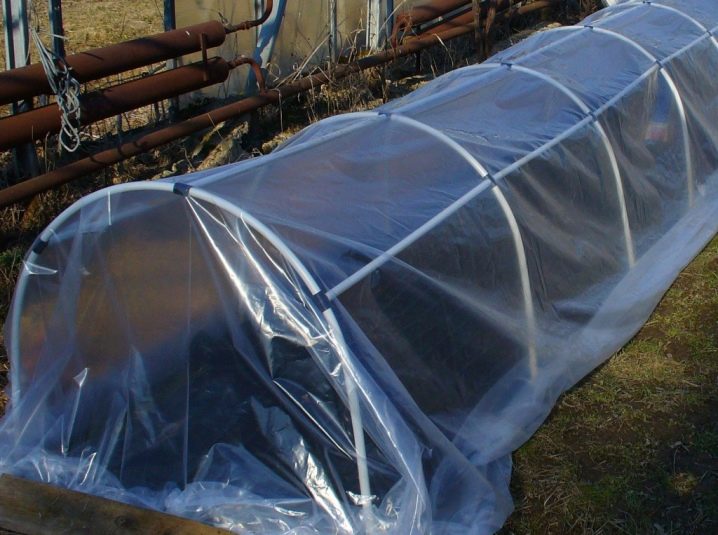
Greenhouse consisting of arcs, is lightweight. Installation is quick and easy. It is easy to move to a new place if necessary. Arcs, which are the basis of the supporting structure, can be metal or plastic. The main thing is that the arcs are flexible and durable.
Today PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is in demand as a material for arcs. It is thermoplastic, is resistant to aggressive environment, low weight and sufficient strength.
Metal arcs are made from pipes, rods and wires of large diameter.
Polypropylene arcs are pieces of plastic pipe. In this case, defining is flexibility, the ability to take an arched shape.
The arc greenhouse is a common ground protection that is used throughout the season. It allows you to successfully grow different heat-loving crops. Plant variety determines the size of the frame. With a height of about half a meter - cucumbers are grown. The height of the greenhouse to one and a half is well suited to pepper bushes, tomatoes and eggplants.
Benefits:
- mobility and lightness;
- does not require a foundation;
- it develops for the winter;
- has a small cost.
Disadvantages:
- covering material is short-lived;
- fragile design;
- difficult to add additional heating or watering.
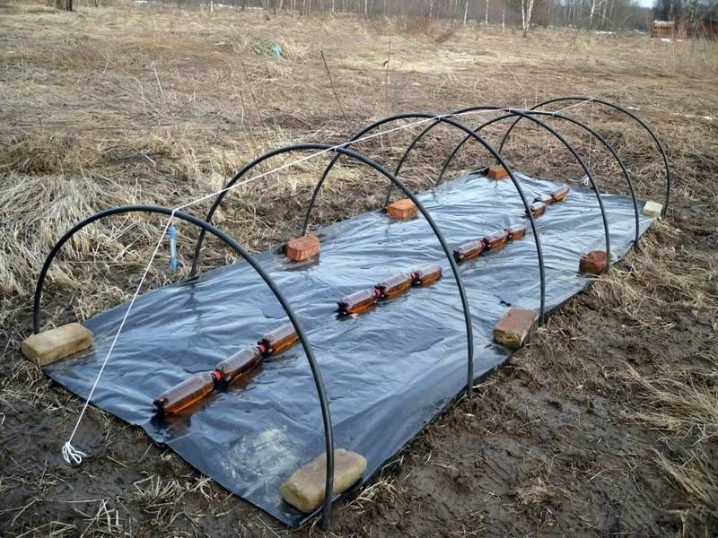
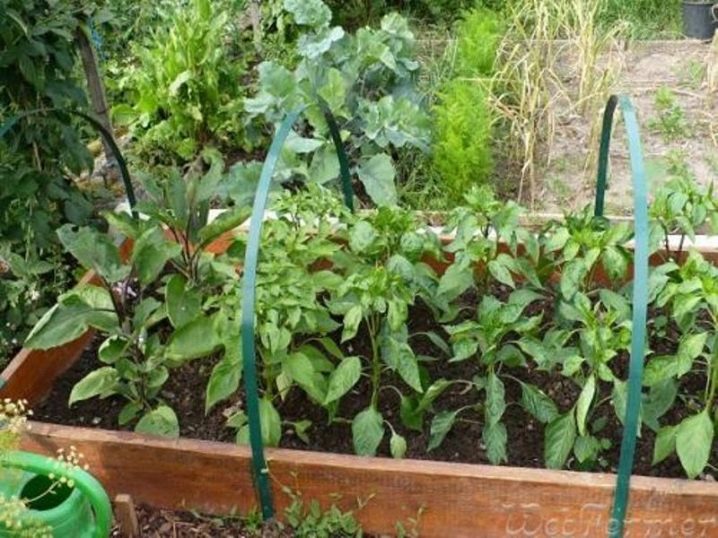
Of old hoses and wires (it is possible to use willow rods) arches for a greenhouse are easily made. The hose is cut into pieces, the base of wire or rods is inserted into it. Pieces are bent in an arc and stuck into the ground every 50-60 cm along the length of the bed.
Similarly used blanks from plastic pipes that are worn on the base of metal pins stuck into the soil. The length of the segments is performed depending on the purpose of the greenhouse. It should be warned against the desire to make a greenhouse height in height of a person - such a structure will be unstable, even when reinforcing the upper part of the arcs.PVC arches require a base of boards to which they are attached.
Frame from metal profile durable and stable. But its production requires special equipment - a pipe bender. We dig up the chosen place on the necessary width. We put the arc - stuck in the ground or attach to the base. We reinforce the construction with ropes, wire, slats, pipes. Cover the frame with covering material. Fix the place of contact with the soil with stones, slats or sprinkle with earth.
On the foundation
Often for frame greenhouse covered with polycarbonate, make the foundation. It provides durability and reliability of the structure, repeatedly increases its service life.
Types of foundations:
- from slag, brick, or concrete;
- from a tree (bar);
- pile
Estimated greenhouse efficiency, time of use, type of crops, cost - the main factors determining the choice of the foundation.
- Slag block, brick, concrete. Excellent base for a greenhouse / greenhouse, consisting of a sand pillow and a layer of rubble. Used on heavy, clayey soils, complicated by groundwater, in harsh climates. For industrial greenhouse complexes in warm and temperate climates make an expensive, concrete foundation. Light soils are suitable for buried greenhouses.High foundations of brick or slag, suggest the presence of a drainage layer.
- Wooden. The features of the material make such a foundation justified only in high, dry places with light ground and good illumination. Usually, a protective structure made of polycarbonate with a long service life is mounted on such a foundation. In order to approximate the service life of the bottom and top of the structure, blocks of wood are carefully treated with antiseptics and solutions that prevent rotting. The tree is laid on a drainage cushion, wrapped in roofing material, or geotextiles.
A simpler option - the finished frame is laid on an aligned surface, on racks of natural stone, or cinder blocks. The supporting components of the protective structure and covering material are attached to it.
- Pile. For critical farming areas, this is the only option to build a reliable greenhouse / greenhouse. The pile construction is universal. Such a foundation is equally effective in areas with active groundwater, frostbite, and uneven surface. Recessed to the required depth of the pile can withstand any design and provide the desired strength.Metal pipes are installed in the wells, inside which are smaller diameter pipes filled with concrete. A crate is put on top of the piles. If necessary, put on top or insulation, or a frame made of wood, which is attached to the frame structure.
Warming up such a foundation, we get a greenhouse for the conditions of a harsh climate, in which you can get harvests all year.
- With walls. Usually it is a box of timber or planks, installed on a foundation or even in-depth soil. From above this basis is closed by a frame from reek, pipes PVC. The design is covered with a film or polycarbonate. For convenience, the frame is attached with hinges. Such structures can be monopitch and gable. The main feature of such a greenhouse is the limited height of the walls (not more than half a meter in order to avoid a shortage of sunlight).
- Frame. The variety of modifications of such structures is limited only by the human creative abilities. The main types are stationary (fundamental) and portable (collapsible). For a framework and protection of the soil and plants are used topical materials in local conditions.The framework is established both on the soil, and on different types of the bases.
Useful tips
- To ensure the right amount of sun and heat, you should position the greenhouse remotely from buildings and trees.
- The ends are located on the east / west line. This synchronizes the biorhythms of the plant.
- You should not choose for the greenhouse much understated and overpriced place.
- The optimal dimensions of width, length, height - 1x3x0.5 m, respectively. Small dimensions allow plants to more intensively absorb and retain solar energy and heat.
- When choosing a structure and materials for a greenhouse, one should focus on finding a healthy compromise in the quality / price ratio.
- The pursuit of cheapness can lead to the fact that the crop will die. Additional operating costs for the replacement of defective parts may exceed the initial cost.
- To ensure an optimal level of illumination, covering material must be kept clean.
Indoor soil is primarily a stable temperature regime, which is necessary for pepper. For the suburban area are relevant two sources of heat:
- solar energy (intensity depends on the purity of the plastic / glass);
- biofuels.
Biofuel is an affordable and efficient way. In his role is used manure. Ensuring the effectiveness of the technique depends on the correct setting of biofuels and site preparation. Additional warming of the side walls is necessary, laying the bottom with straw, on which manure is poured. You can make several such layers. The optimal material for warming the sidewalls - foam.
The choice of organic material for biofuels depends on the time of transplanting. Considered the most productive horse manure. For seven days, it raises the temperature in the greenhouse to 60 degrees and is able to maintain it for two months. After this period, the temperature rarely drops to 20 degrees. This biofuel is particularly effective for early landings. Cow manure and others give a lower temperature.
The use of biofuels makes sense at a pre-prepared place. The thought-over thermal insulation of the wooden, or other basis.
Consider a few additional nuances.
- Growing peppers in isolated greenhouse conditions allows you to create the most comfortable environment and radically protect the culture from the effects of diseases and pests.
- The height of the foundation should not exceed half a meter, this will avoid drying out of the soil and overheating on hot days.
- The recommended height of the arcs is 50 centimeters. Semicircular design is optimal for plants to get enough heat and light.
- Uniform distribution of luminous flux is provided by materials such as polycarbonate and glass.
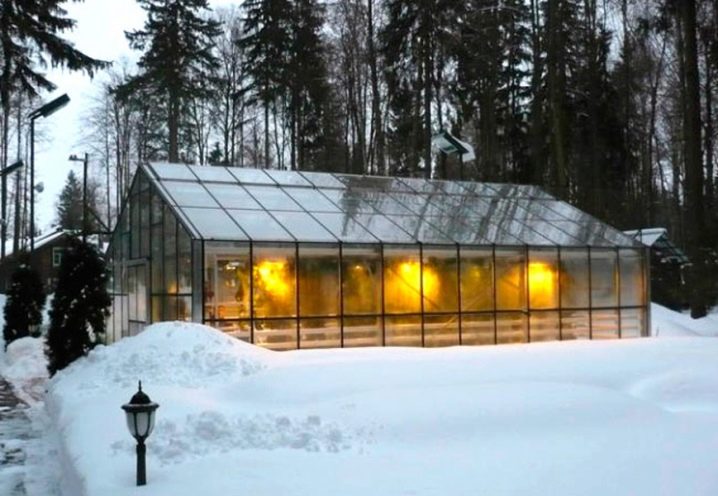
- Protective structures with water heating are usually industrial greenhouses that operate all year round.
- Shed constructions are better positioned so that the line of connection with the loops of the frame and base is on the north side. In this case, the height difference of the sidewalls should be 50-25 cm.
- When installing arc cages, one should remember that the optimal amount is 1 arc per meter of the greenhouse.
- The walls of the greenhouse should be removed from the extreme beds so that condensate does not fall on the bushes of pepper - this can cause plant diseases.
- When installing a greenhouse on the foundation, it is recommended to lay the outer wall of the trench with roofing felt, or with old slate - this will save protected ground from weeds.
- All parts of the structure fixed in the ground need to be pretreated.The tree is covered with antiseptic, metal with bitumen and its analogues.
- When erecting a frame made of metal, the preferred method of fastening components is a bolted joint. Such a structure can always be disassembled and during storage it will not take up much space.
The difference in ambient temperatures can be significant, which has a negative effect on the growth of pepper. Therefore, it is recommended to use heat storage devices. You can use different tools for this:
- plastic pipes;
- PVC sleeves;
- plastic containers;
- a natural stone.
During the day, the device accumulates heat (the coolant heats up - water, stone), at night the heat is slowly transferred to the beds with seedlings. This method is especially effective in the spring when sudden frosts can destroy the entire crop.
Top projects
We have already considered the type of greenhouse, which uses the most simple materials. There are options that make it possible to economically and effectively protect the soil and plants in the summer cottage.
Covering construction of the arcs
This is a portable structure. We choose the material of the frame (metal wire or polypropylene pipes) and its type.You can bend the pipes in an arc, stuck in the ground, or mounted on a wooden base.
To properly set the arc, you need to arrange them in half a meter. Width is easy to calculate, these are four rows of plants. Cover the frame with plastic wrap or other covering material. Below fixation coverage is provided with heavy objects. Between themselves, the arc attached with wire or wooden jumpers.
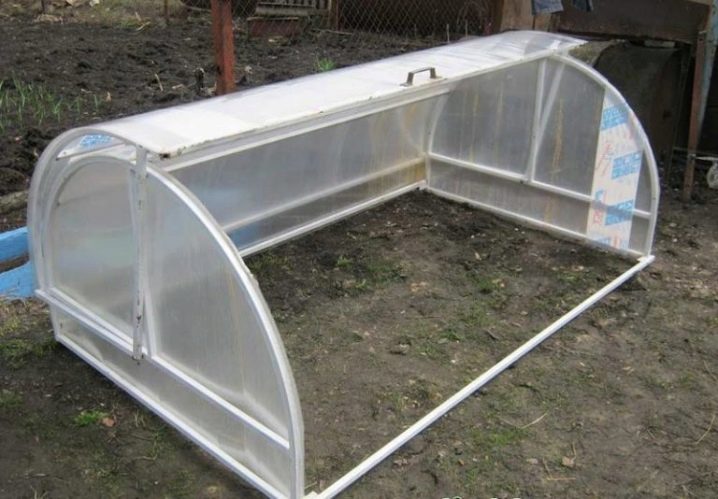
Greenhouse PVC arches on the basis of wood
First of all, the size of the arcs is determined. If the task is to grow peppers before aging on protected ground, 0.7 m will do. The width of the greenhouse may differ in the number of beds. The optimal number of elements and their dimensions are determined based on the length of the structure (usually 1 arc per 1 m).
First, collect the base (timber, planks). Arcs are attached to the base with staples. A greenhouse consists of sectors (70-80 cm.). For durability, the upper parts of the sectors are reinforced with PVC pipes. The design is covered with a film, which is secured at the bottom with a stapler.
Shed construction
In some regions it is more expedient and cheaper to use polycarbonate. Such designs are simple.In many areas, such greenhouses in finished form can be purchased in the store at a reasonable price.
Small frame solutions
These structures are built both on foundations and on buried ground. The selected soil (10-15 cm) ensures the tightness of the junction of covering material to the ground.
PAT
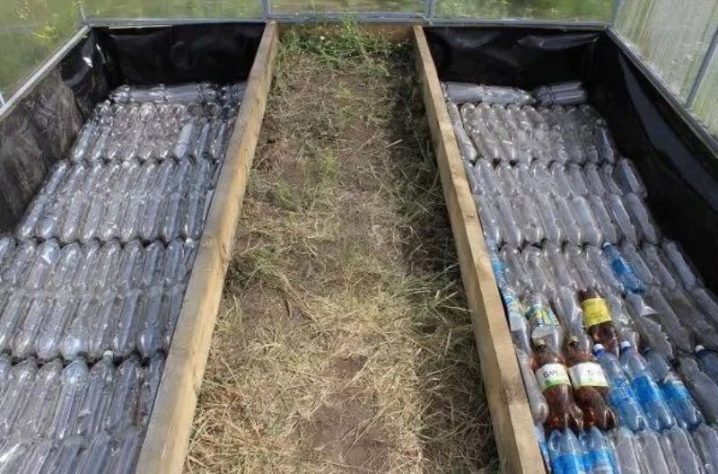
PET (polyethylene terephthalate) is considered one of the best covering materials. This is a polymer from which plastic bottles are made. It is convenient to use a container completely, stringing on metal rods. Constructions that are distinguished by simplicity are either a “book” or a “clamshell”. But, collect and greenhouses such as "house".
Greenhouse / PET greenhouses are quite high-performance. Bottles play the role of light concentrators, ultraviolet reflectors, keep warm well. Additional protection of openings is necessary only in case of frosts.
In the case of plastic packaging, several problems are automatically solved. Such packaging accumulates after the purchase of drinks, its cost is included in the price of the goods, which excludes the allocation of funds for the purchase. With free access to garbage drives, the financial issue is removed.
The uniqueness of the source material allows you to quickly disassemble the greenhouse, replace its parts. Whole plastic containers have a large heat capacity and are characterized by high light conductivity, dissipate ultraviolet.
Calculations
The dimensions of the cleared and leveled area, the type of foundation and construction of the greenhouse determine the required amount of plastic containers. Two main types of such structures:
- from the whole container;
- from the plates.
In the case of whole bottles, the bottom is cut and placed on each other, collecting a “plastic log”. This is the component from which the walls and roof will be assembled. Unique heat insulation and ventilation through the natural gaps of the structure helps to maintain the desired microclimate. Double plastic somewhat reduces the intensity of sunlight.
Plate cut out of the bottle, sew. The resulting sheets cover the design. This method requires half the original material. The light transmission capacity in this case remains high, but the insulation is reduced.
Depending on the type of containers (their displacement), it is calculated how many containers will be taken to cover one square meter of greenhouse and multiplied by the entire area.
Preparation of plastic bottles
We select a place for cleaning and processing plastic. The main device for this procedure is a basin / barrel for soaking bottles. The filled bottles are heated in warm soapy water and kept for several hours. Next, separate the label and leave the container to dry. After that, either the plates are cut out, or the bottoms of the bottles are cut, to assemble plastic logs. The cut-out middle sections of the record bottles will curl, which can be quickly corrected by placing them under an improvised press.
All the talk about growing peppers is reduced to the functionality of a shelter to protect the soil and seedlings. A huge number of existing modifications of greenhouses and greenhouses, when examined in detail, has its own positive features and disadvantages. A clear understanding of local features and the skillful choice of the necessary greenhouse design will help to make the optimal construction for soil protection. Having invested a minimum of funds and having basic tools, you can make a highly functional greenhouse for growing peppers in the summer cottage.
On how to make a greenhouse with your own hands, see the following video.