Technology and ways of laying bricks

Classical technologies are available in all spheres of human activity. In the construction of the classics of the genre is considered brickwork. It has existed since ancient times. There are many centuries-old buildings of burned bricks in the world, therefore, despite the variability of modern building materials, brick products remain in demand.
The technology and methods of laying bricks for each type of construction are different,and the result is one - a beautiful and durable structure.
Brick selection
Brick as a building material with a rich history has been repeatedly improved. The composition of the mortar changed, from which blocks suitable for masonry are obtained, the color and size changed.
These changes naturally led to the fact that about a dozen varieties of bricks with different technical characteristics appeared on the construction market.
Types of bricks are classified according to five criteria: material, purpose, method of manufacture and molding, filling, size.
By production material
Ceramic (red) brick is made from high quality clay. There are no impurities and sulfates, which reduce the strength of the product.
The raw materials for ceramic bricks are molded, then fired and cooled. Firing occurs at high temperatures - 800-1000 degrees. Compliance with the temperature regime is important, otherwise the product will be unburned or burned. In both cases, it turns out second-rate - for the construction of housing, it is already unsuitable.
Determining a marriage is simple: an unburned brick is pale in color, and the burned one is dark brown.
High-quality ceramic brick matte, reddish tint, porous at the fracture. With a slight blow to the surface, it makes a distinctive sound.
Red brick is durable, does not crumble, looks expensive, has a convenient shape and weight for construction. Of the minuses of the material - low heat resistance and the ability to accumulate moisture in the porous structure. In winter, moisture freezes, which can cause microcracks inside the brick. This shortens the life of the brick product.
Various buildings are being erected from ceramic bricks, but it cannot be called universal. You can make a house from it, but for a fireplace or a stove you will need another building material - fire-resistant (fireclay) brick. It is of 4 types:
- quartz (from quartz sand and clay);
- alumina;
- lime-magnesia;
- carbonaceous.
The first two types are inexpensive and are sold in any construction market. They are used for the construction of furnaces. The fire-resistant brick can adjoin to metal elements and naked flame at a temperature of heating not higher than 1300 degrees.
The second two types of fireclay bricks are building materials for industrial furnaces. They can be found on sale, but they will cost several times more expensive.
Silicate (white) brick is made from purified quartz sand, lime without impurities, water. The share of sand is the largest - 80–90%.
Silicate bricks are molded under high pressure and then sent to dry. They do not undergo heat treatment at high temperatures, and therefore are considered less durable than ceramic. Their heat-resistant properties are also low, but soundproofing - at a height.
With such technical characteristics, white brick is not used for the construction of the foundation and supporting structures - it is used for the construction of partitions and internal walls in the room.
The silicate brick may not be white, if coloring pigments are introduced into the composition. They do not affect the quality of the product and “grasp” well on lime and sand.
Hyper pressed brick is molded from screenings (limestone, marble, dolomite, shell rock) and high quality Portland cement. A small percentage in the composition of the raw material is water, which gives the viscosity to the cement and makes it a binder.
Plastic raw materials are pressed in special forms, and the finished brick is used for wall cladding.
The color of the hyperpressed brick depends on the type of screening. It can be yellow, orange, gray, pink, red, milky.
Clinker bricks are made of refractory clay. Clean, plastic, carefully selected raw materials undergo heat treatment. The temperature is so high that the clay melts into a homogeneous mass.
Clinker brick is the most durable, dense, moisture-resistant. It does not freeze inside, therefore it is resistant to low temperatures.
The finished product is smooth, even, varied in color, therefore it is considered universal for construction, except for the construction of furnaces.
To destination
There are three areas of application and three types of bricks, respectively: building, facing, fire-resistant.
Construction (ordinary) brick corresponds to GOST and is suitable for exterior and interior works. From it you can build residential buildings, but without insulation on the walls of the room will be cold. It requires reliable thermal insulation from the inside and finishing work outside, because an ordinary brick has external defects.The rough surface and chips are natural. They do not affect the technical characteristics, but the appearance of the walls is not representative.
Facing bricks are also often called face or facade. It is this type of building material that helps to mask the cosmetic flaws of an ordinary brick. It is smooth, even, rich in color.
Facing can be different material: ceramic, silicate, hyperpressed.
His choice depends on the region of residence: in the wet climate will last longer ceramic finish, and in dry and hot regions it is more efficient to use silicate.
Facing material is of two kinds.
- Textured. In form, such a brick does not differ from the typical one, but it has a relief “pattern”. The edge can be smooth or "ragged." Mostly used for the construction of beautiful fences, finishing buildings. Textured brick can be alternated with smooth.
- Figured. This is a brick with an atypical profile shape. It facilitates work with complex elements, including windows, arches, window sills, rounded corners, fences, arbors of complex shape.It is not easy for a beginner to work with such material, but with its help complex facades of buildings are created.
Facing materials are diverse in color: from milky white to almost black.
Chamotte brick is designed for the construction of stoves, fireplaces, barbecues on the street. They also trim the "apron" (a safe area that protects the floor from ignition) around the stoves and fireplaces inside the room. It withstands repeated heating, contact with fire and coal, but at the same time it has low thermal conductivity. Such characteristics provide it with density and heat-resistant shell.
Chamotte brick is a typical form and figured (for example, wedge-shaped).
By way of molding
Its technical characteristics depend on the method of forming a brick. Modern manufacturers use three molding technology.
- Plastic. With this technology, plastic wet raw materials are used, from which brick is produced in several stages. The finished product is durable, with a high degree of resistance to moisture, but the edges may be uneven.
- Semi-dry. For this method suitable lower quality raw materials.It goes through fewer processing steps and becomes ready building material faster. Due to the heat treatment of raw materials, the quality is not worse than during plastic molding. The edges of the brick are even and the color is uniform, therefore the method is often used for the production of cladding material.
- Manual. Hand-molded bricks belong to elite materials. Although the process is not entirely based on manual labor (some processes are automated for the sake of reducing the cost of goods), the finished product has unique technical and aesthetic characteristics. Such a brick is called "antique" or "aged" because of its characteristic rough texture. It is used for cladding and renovation of old buildings.
The color range is the most diverse.
By the nature of the filling
There are two types: corpulent and hollow.
Solid bricks have only natural voids (pores). In relation to the total mass of the product, their percentage is not more than 15% for ordinary material and not more than 5% for facing material.
Bearing structures are erected only from solid brick.
There are 4–8 chambers in a hollow brick, in percentage terms - these are 25–45% of the total mass. Cameras are needed for thermal insulation and sound insulation, so the material is used for the construction of partitions and walls. Hollow brick is not suitable for the construction of supporting structures and furnaces.
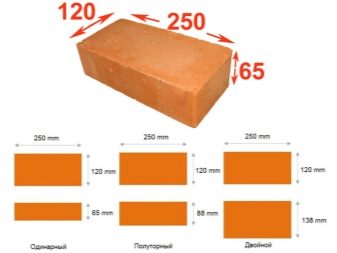
To size
The size of the brick is also an important characteristic. It helps to correctly calculate the step of laying and the amount of building material.
Russian GOST provides three standard sizes:
- 25 cm - in length, 12 cm - in width and 6.5 cm - in height;
- 25 cm - in length, 12 cm - in width, 8.8 cm - in height;
- 25 cm - in length, 12 cm - in width, 13.8 cm - in height.
In all respects, deviations up to 4 mm are permissible.
European dimensions are more variable.
Regardless of the size of the brick has 3 faces: bed, poke and spoon part.
The bed is the largest working area of the product. On it a brick is laid in rows.
Spoon part is called the longitudinal side face. It can also serve as a working party, but less often.
Tap - the smallest in area of the product.
These terms need to be remembered in order to navigate the lessons for beginner masters.
In addition to these parameters, you need to consider the brand of bricks, strength, resistance to weather conditions. Before large-scale construction, it is recommended to study similar structures from different types of material, estimate the service life and operational condition of the products.
Required tools
Brickwork is impossible without auxiliary tools. They are divided into two categories: measuring and working.
Inspection tools are needed to lay laying smoothly and correctly.
- Plumb. Structurally simple, but important thing to control the vertical surfaces of the masonry: walls, walls, pillars, corners. Plumb looks like a durable lace with a sinker at one end. The weight of the sinker may be small (200–400 g) to control verticality at the level of one floor.
To measure correctness at the height of several floors, a more weighty load is needed - from 500 to 1000 grams.
- Level. Aluminum tool that serves as an auxiliary element for checking vertical and horizontal lines of masonry. On the body of the rule there is a flask with non-freezing liquid and an air bubble. Horizontal and vertical checked by bubble deflectionfrom the central position.
- Berth This is a thick thread or 1–3 mm thick twisted cord. Berths stretch between the corners-beacons, so that the rows of masonry were even along the horizontal line. It provides the same thickness of the mortar joint and a clear horizontal. It is not enough for one mooring to moor - a self-made load is needed so that the thread is taut and a nail 3–4 mm thick. A half of a brick wrapped in paper and a bag with handles are suitable as a load (to tie up the ends of the mooring). Nail is needed to fix the thread between the bricks.
- Rule This tool looks like a spatula with a blade length of about 100 cm or an aluminum rail up to 150 cm long. The rule is needed to check the face of the masonry. It should be as smooth as possible.
- Order. This is a wooden batten with markings for a typical brick and a standard weld with a thickness of 1.2 cm. A division with a distance every 77 and 100 mm (thickness of the brick + weld thickness) is applied to the rail. With its help mark the rows, window and door openings, floors and lintels.
- The bar. Auxiliary metal profile of different shapes.It is made of thin stainless metal and helps to make even corners and openings. The bar remains inside the masonry, in contrast to the mooring, which moves upwards from row to row.
Working tools are a necessary base for self-laying.
- Trowel. This is a small spatula with a wooden handle and a polished steel work surface. The steel part is diverse in shape and size (drop-shaped, triangular, rectangular). As a rule, it has a broad base and a narrowing tip. Trowel is needed for leveling the solution at the seams. Also with its help fill vertical seams and cut off excess solution.
- Spade mortar. The name of the tool already informs about its functions - stir the solution in the tank and feed it to the seam.
- Patching This small tool is needed in order to give a certain shape to the seam. The jointing can be convex and concave for projecting and “recessed” seams.
The width is selected in accordance with the thickness of the brick and the thickness of the layer of mortar.
- Hammer pickaxe. It is a hammer with a pointed end on one side and a flat part on the other.With it, the brick is divided into parts when necessary.
- Mop Tool with metal handle and square rubber plate at the base. The location of the rubber is horizontal. Mop is needed to smooth down and fill the seams inside the ventilation channels. It also removes excess solution from the ventilation ducts.
In addition to the two main categories of tools, additional auxiliary tools are needed: tanks for mortar and water, cement and sand, gloves, a safety kit for working at height.
The basic principles of the process
The technology of brickwork - these are key points that are considered common for the construction of any objects. The subtleties of the process may vary when choosing one or another method of laying, but to master the basic techniques is necessary.
First of all, it is important to determine the type of foundation and masonry width. The height is calculated by a special table that contains information about the thickness of the brick, the corresponding thickness of the mortar and the number of blocks per 1 square meter.
The foundation is required for any heavy construction. For non-residential facilities in one floor is enough column foundation.Reliable house is better to install on a ribbon or solid foundation. Brick is considered a heavy material, so it needs a solid base. The higher the storey of the house, the stronger should be the foundation.
Thermal insulation and sound insulation properties of the building, as well as its refractory properties, depend on the thickness of the masonry.
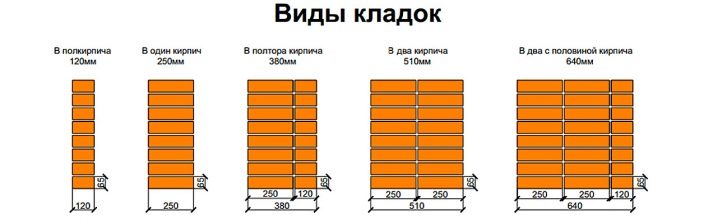
There are 5 types of masonry thickness.
- In half-brick The thickness is equal to the width of the bed - 12 cm. This option is suitable for non-residential one-story buildings.
- One brick. The wall thickness is equal to the length of the bed - 24-25 cm. Enough for a single-story home with thermal insulation.
- One and a half bricks. The thickness of the structure form two rows of blocks. It is 36–37 cm, respectively. Such masonry will be reliable for one-story and half-story buildings.
- Two bricks. This option consists of the length of two beds - 48–50 cm. You can safely build a two-story cottage on a solid foundation. The total weight and cost of such a building is quite high.
- Two and a half bricks. The wall thickness is 60–62 cm. It is rarely used for multi-storey residential structures. In addition to the large weight, such a building will require investments in the heating system.
Warm up the brick walls in the winter is not easy.
Having determined the required width and type of building material, you can begin to build a foundation and lay a brick. In the process you need to follow the rules.
- Use fixtures to control horizontal and vertical lines so that the masonry is flat. The most important stage is to lay out the first row correctly.
- First, build corners, then the middle part of the wall. The corners serve as landmarks to lay out even horizontal rows.
- The direction of the masonry is from left to right.
- The blocks are placed on the mortar in such a way that in the horizontal rows the upper brick rests on the two lower ones. The support area is not less than one quarter of each of the two lower blocks.
- The solution is placed on the horizontal and vertical seams. This protects the brickwork from cracking.
- Required element masonry - ligation. It guarantees durability and protection against delamination.
- For additional strengthening of the building metal reinforcement is used.
- Between the masonry and the foundation necessary waterproofing (roofing material or mortar).
- If you plan to plaster the wall, the joints do not need to be completely filled. So plaster better grab.
- Facing and working bricks are laid out according to the same rules.
Mixing technology
The composition and consistency of the solution depend on the design and technical characteristics of the brick. Four types of masonry mortars are common: cement, lime, cement-clay, cement-lime.
Cement mortar is familiar to many on the floor filler. In the form of an intermediate layer in the masonry, he retained some properties of the screed: it is cold, durable, and inactive.
Preparing a solution of cement, sand and water. Depending on the brand of cement, the proportions in the composition vary: from one to six parts of the sand of the middle fraction fall to one part of the cement.
To get a quality solution, you must first thoroughly mix the dry components of the composition, and then gradually pour in water. Thick mass is mixed to a uniform consistency. The solution should not be too thick or too liquid.
Cement-sand mortar can be used for masonry, but this option is not the best. Cement - sedentary material.
The seam is obtained too hard and less resistant to temperature fluctuations,therefore, laying on the cement joint wears out faster.
Lime mortars are considered the warmest, but inferior in strength to cement. Due to their low strength, they are used in the construction of single-storey buildings, indoors.
To prepare the solution with your own hands you need a lime "dough" or quicklime. Lime is mixed with sand in a ratio from 1: 2 to 1: 5.
For beginners there are ready-made mixes. They just need to add water, following the instructions on the packaging - just how to dissolve wallpaper glue.
Lime-cement mortar (sand, cement and lime) has all the necessary qualities for a reliable result: it is universal for all types of bricks, moderately plastic, easy to apply, adheres well to the surface of the working material.
Preparing lime-cement mortar on the lime "milk" (slaked lime, diluted with water). Then the sand is mixed with cement. The mixture is brought to a flowing consistency with lime "milk" and stirred.
This type of mortar is universal for all types of brick buildings.
There is also a variety such as cement-clay mortar.The ratio of clay and cement in the dry mixture is 1: 1. Then the solution is kneaded into a homogeneous mass. Its main difference and dignity is fast setting at low temperatures. And besides this, he is not afraid of moisture.
Regardless of the type of material and solution, there are general principles for working with it. So, for example, the surface of a brick matters. The more porous it is, the more moisture will be absorbed into the brick when it hardens. The laying quickly hardens, seams become strong. This must be considered when preparing the mixture.
To avoid stratification of the solution, it must be periodically stirred.
There is no need to dilute the solution to the whole object: it quickly hardens. It is better to prepare the mixture in portions, working on small areas.
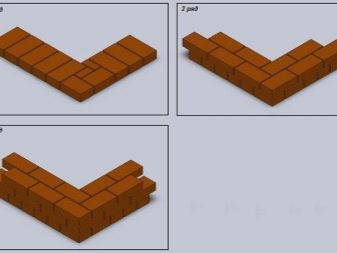
The details of dressing stitches
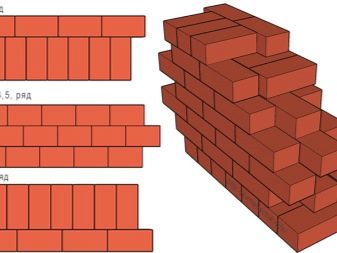
For beginners, the words "stitch" and "ligation" raise questions. In fact, to understand this topic is easy. The idea of building dressings is already reflected in one of the basic principles of masonry: for a wall to be strong, each brick in the top row must rest on at least two bricks from the bottom row. Sometimes this technique is called “hacking”, that is, the vertical seam must form a zigzag, rather than a straight line.
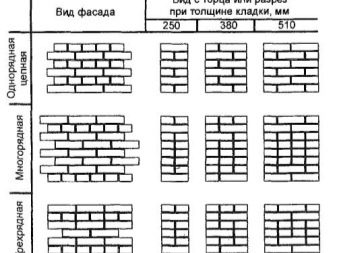
Modern construction has not one, but three ways of dressing: chain, three-row and multi-row.
Chain ligation (also called single-row) is the ordinal alternation of spoon and pinch rows, that is, one row is laid out by the spoon side (long), and the butt row is built over it (short side).
Recommendations for chain dressing:
- the first row, from which the laying begins, and the last, finishing, must be poked;
- the bricks in the spoon row rest in at least two lower bricks, the longitudinal rows (vertically) should not form a straight line;
- the longitudinal seams of adjacent rows are shifted by half a brick (relative to each other), and the transverse ones - by one fourth.
Chain ligation is considered the most durable and reliable, but at the same time it is the most energy-consuming and expensive. During the work you will need to make a lot of incomplete fragments. Some of them will be a marriage in the process of mastering a brick hammer.
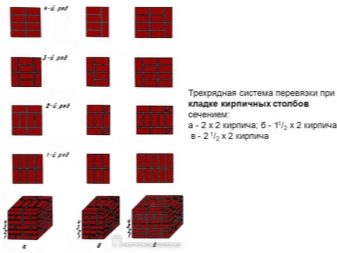
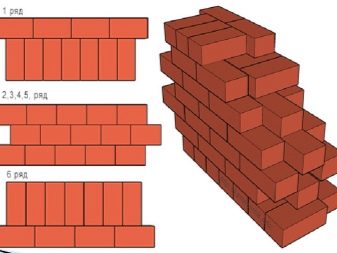
Three-row ligation is a laying according to the scheme, where every fourth row is tychkovy. It is carried out simply: the first row is a tychkovy, then three spoon ones, again a tychkovy and so on.Closes tychkovy number. There should still be two points of support for the brick in the top row.
Three-row dressing is indispensable when working with walls, columnar foundation, columns inside the room.
Multi-row ligation on the principle of masonry construction resembles a three-row lining, but with the difference that the butt row appears not after 3, but after 5-6 rows of rows. At the same time a small amount of incomplete bricks leaves, and the design is as reliable as possible.
Multi-row ligation is needed where it is important to provide good thermal insulation in the room. But for the walls and posts it is not suitable.
The thickness of the ligation, as well as the thickness of the masonry, varies from ½ to 2.5 bricks.
Popular masonry methods
Under the method of laying at the same time understand the way the location of the bricks in a row, design features (with voids, reinforcement, without voids) and decorative features.
Putting bricks in three ways: pressing, sprinkling and sprinkling with undercutting solution.
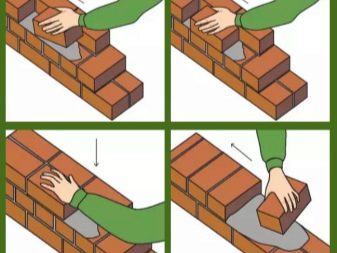
Tight
- Prepare moderately thick solution (so that it is convenient to type and level the trowel). Suitable cement.
- Spread the mortar under the first brick, departing from the front of the erected structure 1-1.5 cm.
- Install the first brick on the bed, tightly pressing it to the base.
- Collect excess mortar with a trowel and press it to the loose butt edge.
The next brick will join this place.
- Holding the metal part of the trowel pressed to the butt of the previous brick, hold the new block with your left hand and place it next to the first one.
- Quickly pull out the trowel. The solution should remain between the two butts.
- Lay out the entire horizontal row in the same way, cutting off the excess solution every 3-5 blocks.
The result is a smooth and durable brickwork. From time to time the vertical and horizontal walls need to check the building level or use a mooring.
This method may seem complicated to a beginner because it requires a lot of unnecessary repetitive movements.
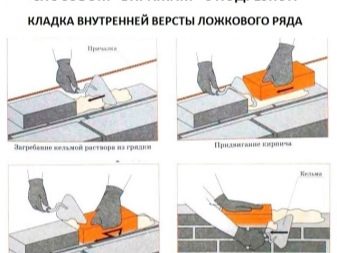
Sprinkling
- Prepare a plastic solution. For example, lime-cement.
- Line the solution with a trowel, stepping back from the edge of the front side 20–30 mm.
- Install the first row brick. For an even row it is better to start with the construction of corners.
- Take a second brick, fix it at a slight angle to the seam.
- Remove the trowel excess mortar, which protrude from under the first brick, put it on the ground, smooth out.The bricks are popped into the plastic mortar by the plastic solution. The excess solution will fill the gap between the buttings.
- Lay in the same way the whole row.
Laying a sprinkler is faster and easier for a beginner to master. Laying a brick can be on the bed, and on the edge (spoon part).
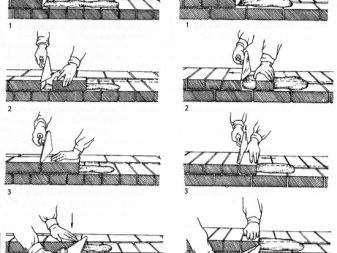
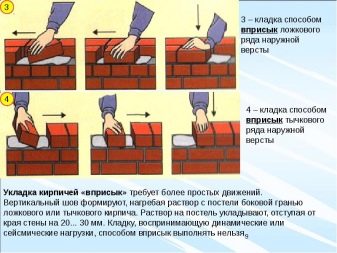
Injection with undercutting solution
It differs from the identical one in the name of the technology only in that it is necessary to retreat from the front part of the wall no more than 2 cm, and the solution is not cut off after 3–5 bricks, but after each laid element. So laying looks more accurate.
In terms of masonry design, three kinds are popular.
- Lightweight. Masonry with voids inside the walls under the insulating material. It is used for the construction of low-rise buildings.
- Reinforced. Masonry using steel mesh, which increases the reliability of the structure. Actually in seismically active regions and with the lining of a working brick facing material.
- Classic. Use of masonry with dressing of a particular type.
In the classical way, the walls of houses are erected, cellars, gazebos and household buildings are erected.
Decorative laying
- Ornamental - this is the formation of a pattern with the help of bricks of different colors (for example, plaster and red). Common patterns: Dutch laying, cross, chaotic, Flemish, spoon with offset.
- Bavarian - German technology, the essence of which is the use of bricks of different shades of the same palette. Pattern in the alternation of colors is missing.
- Facial - Facing the facade in half-brick using decorative elements. You can often see a beautiful facing material with the selection of individual elements (base, eaves, slopes) decorative plates.
- Openwork - brickwork with relief. On the background of a smooth wall there are protruding fragments. Also, the openwork masonry implies that there is a gap between the bricks of the adjacent bricks, as if the wall is “woven” out of bricks.
Safety in the performance of work
The predominant type of brick is residential buildings. And the erection of the wall, even low-rise building implies working at height. For safety reasons, it is not recommended to carry out laying while standing on the wall being erected.For work, we need special platforms that are below the level of the wall being erected.
At a height of two floors for work need interfloor overlap.
Before starting work, be sure to check the tools for serviceability. Handles must be free of burrs and defects, fit firmly and correctly. Gloves or gloves are recommended to protect hands from damage. Working equipment must comply with weather conditions.
Tips for the novice master
Skill in any business requires training. A common mistake for beginners is to take up full-fledged construction for the first time. The ideal result without practice is achieved by units, therefore the most important advice to beginning bricklayers is to train on simple objects and available materials.
For this purpose, perfect cheap brick, trowel and plain tile adhesive. Unlike the solution, it seizes more slowly. The construction of bricks on glue can quickly disassemble and repeat the work on the bugs until then, until you come to an understanding of how to put the bricks in one way or another.
Learn how to make high-quality masonry, for example,having built a flower bed for a garden or a column foundation for an arbor, and after starting to build a new summer house of brick.
In the following video, see the mistakes that novice bricklayers have in brickwork.