Foundation construction: step-by-step instructions for making their own hands
The construction of any home, bath or even just a barn always begins with the preparation of the foundation. But to make it rather difficult, there are quite a few potential problems that every builder, be it a professional or amateur, is obliged to exclude. For a start, it is worth understanding what the basement under the house actually represents.
What it is?
The foundation is an underground, much less often an underwater part of any structure, transmitting static and dynamic stresses onto a soil foundation. Proper design implies a transfer of impulses in which it is impossible to exceed the norms of shrinkage and accelerated destruction of the house.
There are a number of techniques by which this effect is achieved:
- distribution of active forces over a considerable territory;
- removal of soil to a strong mass;
- overcoming loose layer in some places due to piles;
- increase the strength of the surface array.
The easiest option is to build on completely rocky ground, there is no shrinkage there, or it is too small. It is much harder to create and design foundations where the soil is characterized by high compressibility. Even worse for architects and developers of the territory with varying properties of the soil.
The type of substrate determines the preferred options for the base of the house. The contact space is calculated based on the emerging load and the projected response from the ground.
Species
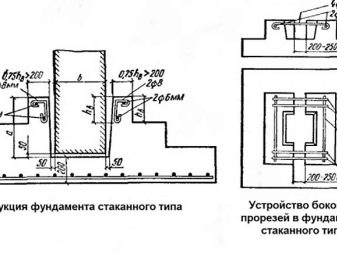
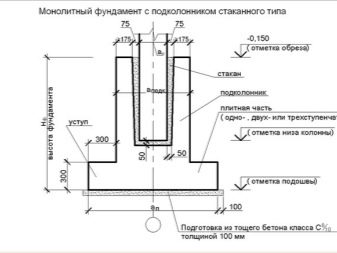
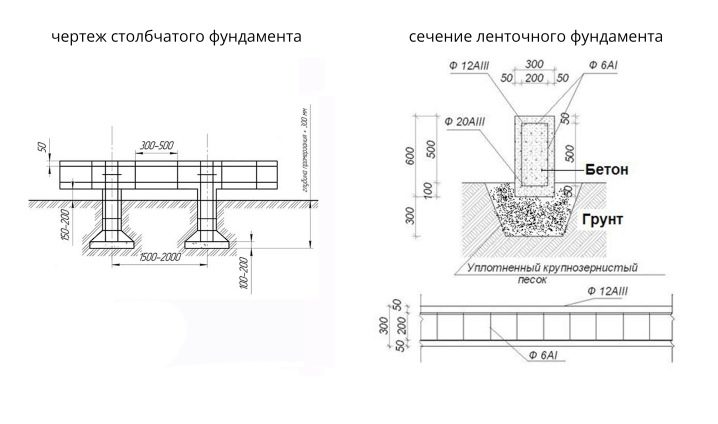
In household low-rise construction a much smaller range of foundation options is used than in the industrial sector. That is why it is possible and necessary to study each type most closely in order to prevent the occurrence of errors. Along with ribbons and slabs of monolithic execution, glass-type bases have also become widely sought after. The name is not accidental - an overload takes on a dotted structure, then this force is distributed exactly where the pressure can be very large.Under the large buildings of small height it is “glasses” that are mounted in many cases.
Important: do not take the name of this foundation literally. Geometrically, it most closely resembles steps in the form of trapezoids, the peaks of which are already compared with the base.
It should be noted that under low-rise buildings glasses should not stand in principle.
They are preferably placed under:
- bridges thrown over reservoirs;
- transitions and crossings over rail tracks;
- underground garages, parking lots;
- single storey warehouse, sports, entertainment and trading institutions;
- workshops and ancillary facilities in energy enterprises.
Stakannye foundations are formed strictly in the framework of the technical specifications and GOSTs, there can be no amateur initiative here in principle. Determining the properties of the soil and material, drawing up a picture of geological formations is carried out by thorough tests. For each specific case, design institutes develop special series of glass foundations, the features of which are fixed as strictly as possible.
Key component details are:
- plate, which plays the role of support, is installed on a pillow of sand and rubble, occupying the bottom of the pit;
- column;
- podkoladnik, just he looks like most of all on the glass;
- a pillar of concrete holding support beams under the walls.
Heavy reinforced "glass" dots, and therefore the load on the soil is minimal. The speed of work is impressive, even quite well acquainted with the construction. Moreover, the need for special machines when lifting heavy parts does not adversely affect the timing of the work. Low severity of contact with the ground allows to minimize water absorption. Under buildings of considerable size, the “glass” is very good, but under the private house it does not justify itself.
Glazed foundation can not be done if you do not clean the surface properly to a perfectly flat state. It is forbidden to lay the slab above 1 m. In the process, the geometry is constantly monitored using levels and levels. Glasses after delivery to the construction site is cleaned of any debris, lifting and installing them are made using a crane. You need to work slowly, carefully checking the positions of the scratches.
Grid of thread will help to link the individual elements. The removed soil cannot be removed, it is useful for backfilling the excavation to the top of the mounted unit. Next, put the support beams on the glasses themselves or on the posts.
The use of wedges under the columns of industrial buildings is strictly necessary. In the private and individual construction of a "floating" type of base.
Of course, there should be no fluid in it or around it. On the contrary, the structure being created is a rigid, reinforced slab of reinforced concrete, located under the entire volume of the future house. "Swimming" is reduced to the adaptation of the support arising loads. Such a solution almost does not change under the action of ground movements, unlike metal pipes (piles); they are not deformed by cold heaving forces. In most cases, plates of 25-30 cm in thickness are used, under which there is a layer of sand and gravel of comparable size.
A serious problem with any floating grounds is a significant consumption of building materials. It is impossible to fill the slab where the territory has at least a different slope from the measurement error.And even in the most favorable cases it is not possible to organize a basement or basement room. Requirements for communications are becoming more stringent, their wiring and planning become filigree art. Moreover, if mistakes are made with the infrastructure, the complexity and cost of their correction is unacceptably high.
Materials
Much when choosing the type of foundation and its optimal organization depends on the type of building materials used at the top. So, a brick wall is heavier than a comparable (or even slightly larger) wooden structure, so you need to create a strong, stable base under it. A building with a deep foundation of a support is recognized by most experts as the most reliable and sustainable, but the complexity of preparing such an element makes it acceptable only for a large brick house.
In addition to concrete strips, three types of piles are often mounted:
- bored;
- screw;
- hammered
Even without special geological and geophysical studies, it is obvious that the properties of the soil in different places are not the same. Its composition and mechanical parameters directly affect the choice of the optimal and permissible type of material.
Also it is necessary to take into account the freezing zone, the characteristics of the above-ground structure, climate, groundwater, means available to the developer.
- reinforced concrete;
- asbestos pipes;
- metal constructions.
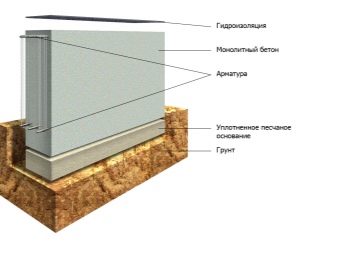
But the wood, even particularly durable and processed according to all the rules of protection, cannot be recognized as quite an effective solution. In most cases, independent developers choose reinforced concrete, because this material is universal and suitable for all known types of soil. It can be prepared using cement, sand of various fractions, gravel and reinforcing rods. Installation of steel strips is done in the formwork, after they are connected, mortar is poured inside.
By changing the proportions of its components, the consistency and adding special additives, you can flexibly adjust the properties of the finished casting.
During the construction of buildings on strong soil, composed of rocks, can be used for laying the foundation of natural stone and light varieties of buttobeton. The same materials are recommended for use on most soils that are not subject to heaving in the winter.But it should be noted that compliance with the work methodology becomes critical. The incorrectness of the contours of natural stones makes it difficult for them to uniformly lay out. It is very difficult to correct the detected deficiencies; for this, you almost always have to call lifting equipment.
Therefore, simple concrete is chosen much more often (even without reinforcing reinforcement inserts). As a binder, in addition to cement, polymers of a special composition and the combination of silica with lime are sometimes used for the production of concrete. But the latter type, which allows making silicate concrete, shows itself very poorly where the soil is abundantly saturated with moisture or exposed to freezing to great depths.
Instead of filling it with your own hands, you can install ready-made blocks, but this is a less accurate and reliable way. Industrial semi-finished products are needed for pillar and strip foundations.
Much attention is, of course, paid to the sand. In addition to being part of the concrete solution, it is “marked” in another role - the underlying pillow. Such linings are recommended to be created if the rocks below are friable and by themselves will not bear the emerging load.Both cases, when sand is used in the construction of the foundation, require mainly its career variety with a large fraction. As reinforcement, special rods are used, the geometry of which is designed for perfect adhesion to the concrete mass.
Wood is used in the form of supports in the formwork structures. The cheapness and availability of this material does not allow, unfortunately, to ignore its main problem, that is, a short period of operation. Choosing a natural stone, you should carefully understand not only its characteristics and cost, but also with transportation costs. The quarry stone is cheaper and more practical than granite or sandstone, you can get it without excessive expenses. For warming foundations, claydite is traditionally used, but it makes sense to think about other, more modern and practical insulation materials.
Special features
The design of a particular foundation to a very large extent depends on the type to which it belongs. For low-rise private building is characterized by the entire range of classical bases and their combinations among themselves. The slabs are invariably cast only inside the formwork; they cannot be used on a steep slope and on subsiding ground.Assembling pillars from concrete racks and glasses does not exhaust all possible options; it is quite possible to cast the solution into a tubular or shield formwork. This formwork has a very wide lower part, but its carrying capacity is less than that of a pile.
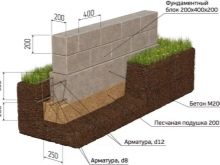
The tape base can be assembled from the foundation blocks FBS, lined from rubble, decorated with brick or embedded in the formwork.
If the soil is prone to swelling, the tape requires:
- drainage works;
- backfilling non-metallic materials;
- thermal protection of the most problematic parts of the structure.
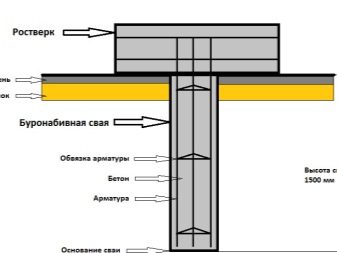
As for piles, each subspecies has specificity. So, bored execution well manifests itself in areas with difficult terrain or with weak soil. But at the same time, the lack of waterproofing makes it impossible to use such supports with medium and high levels of soil water. Screw supports have no technological limitations, but it is recommended to use them only under wooden buildings.
All pile and pole foundations are supposed to equip with a grillage, it can be done in different ways, but in any case it is intended to become a support for the walls and increase spatial rigidity.Under the stairs located in the house, emergency power generators, furnaces, capital fireplaces, and so on, it is required to organize autonomous foundations.
When an extension is constructed, it is advisable to give preference to solutions on piles and on pillars. Regardless of whether these or any other types of bases are chosen, it is very important to leave a technological gap between the main and secondary foundations.
For your information: the roof systems of the roof blocks must also be autonomous. The column system is attractive for its exceptional simplicity and the ability to perform almost all the work without assistants. The post is supposed to be poured at one time.
The composite structures of the foundation, assembled from pillars, are:
- plates 0.3 m thick;
- reinforced concrete racks;
- reinforcing vertical frame;
- grillage of various materials.
With all the virtues, the pillar version will not cope with the load from the heavy walls. It will work poorly on wet soil, on soil prone to subsidence and creep. It is not recommended to use a similar approach where there are steep slopes.But swelling is not too dangerous, it is enough of a typical set of measures to prevent it.
Pillars are better than piles in the sense that they allow for additional formwork and waterproofing after construction.
Private developers appreciate the ribbon foundations with a small depth. It is much more difficult to equip them than any poles. For reinforcement, frames are used, the junction points of which are reinforced with anchors. To make the outer layer of concrete last longer, liners and side rings are used.
Additional cover provide:
- waterproofing layer;
- insulating materials on the outer edge;
- blind area (preventing swelling);
- non-metallic materials (for the same purpose);
- backfilling of trench sinuses (so that the tape is not pulled out to the surface).
You need to deepen the tape only if you have basement floors. In any case, it does not apply to subsiding and wet soils. If construction is carried out on a slope, stepwise concreting often helps, but even it does not allow to install heavy-weight walls with confidence. The undoubted advantage of the tape is the convenience of working with points of entry of engineering communications and the absence of restrictions on the height of the house.Floors can be built on the ground, we also allow the installation of ceilings on beams. In the most difficult cases where the tape, poles and piles are ineffective, it is recommended to use plates.
It should be noted that even this very reliable technology has objective limits. If the soil has a low resistance, the slab base may subside. Under the action of heaving forces arising on the overhanging slope, the block can move to the side. The floating slab is characterized by the identical thickness of the perimeter and requires a significant consumption of building materials.
The ribbed version allows to reduce the thickness of the central region; There are also solutions with built-in underfloor heating and with the preparation under the cellar.
Regardless of the option used, all foundations must have air flow. Underground continuously accumulates moisture evaporating from the ground. Water vapor is very dangerous for any building structure, for any finishing material. Increased attention should be paid to buildings made of wood and all kinds of houses in areas where radon accumulation is likely. The absence of soil freezing causes moisture to leak underground even in winter.
If you do not take care of the products, the water will collect and freeze on different parts of the foundation, on the reverse side of the floors of the first floors. SNiP provides that, even in ideal cases, the total area of the ventilation ducts should be at least 0.25% of the basement space or the technical subfloor. And when work is carried out in areas with a high level of radon concentration, this figure increases by 2-3 times. Additionally, it is worth considering that equip products less than 0.05 square meters. m just does not make sense. Their maximum value is 0.85 square meters. m, since if you exceed this size will have to carefully reinforce the structure.
What forms do the food - decide themselves homeowners. Most often choose a rectangle, this configuration is not only simple, but also the most aesthetic in appearance. But the location of the holes outside should be uniform in area. It is possible to exclude the formation of non-ventilated “bags”, if you do not move away from the corners of more than 90 cm from the corners (measurements are taken along the inner faces). The most effective solution is a symmetric arrangement of an even number of holes.
How high to deliver the airways is determined according to the height of the first floor above the ground. But their lowest point should not be closer to the ground than 20-30 cm. If you do not follow this rule, you can face the underground bay in the spring and autumn months.
Important: when the house is equipped with internal bearing walls, it is necessary to make airways for each underground space. If the calculations result in an unnecessarily large number of holes, which can weaken the design of the foundation, it is necessary to circumvent this problem by increasing the size of the individual channel.
In addition to ventilation, rational arrangement of the foundation implies backfilling. Houses of permanent residence, heated all year round, do not allow them to freeze through the underlying soil. Therefore, under such buildings is allowed to use any type of dumping, even from clay. Projects in which it is planned to conduct overlapping on beams, it is recommended to fill it from within with clay as the cheapest material. The sand will have to be used under floating floors as a layer of at least 100 mm.
Significant amounts of construction work make it quite justifiable to fill it with soil from the building patch removed from the trenches. Only the upper part can be filled with sand to fill footing.In areas with high groundwater levels, crushed stone is used. If the aquifer lies relatively deep, it is allowed to save using sand.
For your information - the organization of external clay castles described in the building codes of outdated editions is now prohibited.
Compaction of the soil to be filled is mandatory every 0.2 m. The presence of large stones in the backfill (over 0.25 m in size) is unacceptable. Drainage, if necessary, is formed in the form of longitudinal channels that are connected to a single circuit, standing along the entire perimeter of the building. To lay a foundation with non-metallic materials at different depths. Thus, with episodic heating of the house, 0.2 m of sand near the inner walls is enough.
If there is no heating and the soil can freeze through by 100 cm, it is required to form a sinus 200 mm saturated with inert materials. But when the freezing depth reaches 2 m, 50 cm of the protective layer will have to be put.
Important: the counting of this depth of backfill is taken from planning marks, most often from the blind area. It may not exceed ¾ recesses of the soles of the bands. Only when forming overlaps in logs it is allowed not to condense the buried materials, in all other cases it is extremely important.
Under the screed it is required to always seal the filling to the level of 0.95 m. It is necessary to finish tamping, whether in manual or mechanized mode, after leaving no trace on the ground. Watering sand, loam and sandy loam is impractical, it can lead to excessive saturation of the soil horizons with water. Heavy soil can be moistened to no more than 23%, and light sandy clay with a maximum of up to 14%. In any case, it is unacceptable to mount the screed before the soil dries completely.
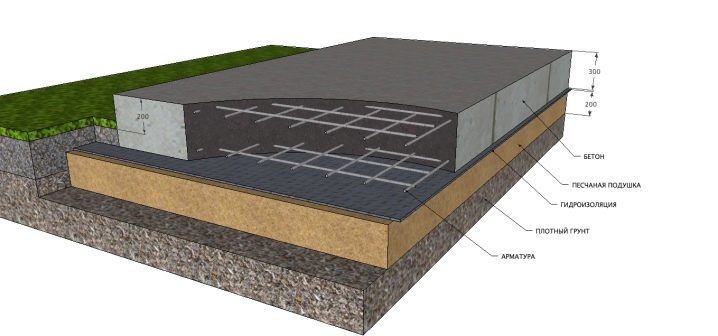
Footing should be used under all monolithic foundations.
Her role is threefold:
- reducing the height of the protective layers;
- elimination of breakthrough of cement milk in the lower layers;
- cover waterproofing basement soles.
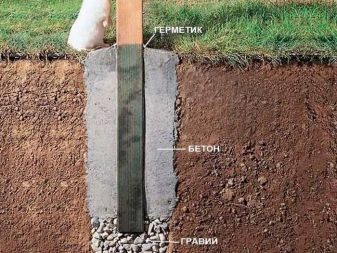
The soil, located along the outer edges of the basement, is not protected from the cold. This means that it will swell, and non-uniformly throughout the volume, and there will be a force pulling the concrete base upward. There are three main solutions to this problem, one of which is backfilling. You can also warm the blind area, forming a tape of 0.6-1.2 m wide around the entire house. Another way is to create a sliding-crushable insulation.
Its essence lies in the fact that rigidly extruded polystyrene foam is attached to the outer walls. Next, the base, fixed in the ground, covered with a pair of layers of polyethylene. Sheets PSB-25 are mounted, they should be placed strictly vertically and tightly against the wall. Sand sheets will be able to hold these sheets, so no additional attachment is required. Heaving forces invariably crush polystyrene, but its rise over a layer of smoothed film does not damage the key level of thermal protection.
Returning to the sole under the foundation, it is worth noting that most often it is twice the width of the base. In order to rely on the entire length of the sole could stably, equipped with the so-called footing (other functions of which we already went). In industrialized countries, this support structure is prescribed by all building standards and technological standards. Double-rechecking of all distances between landmarks placed by land surveyors helps eliminate errors. Only then all installation lines are shown with cords.
Paving made of rubble allows you to save on construction work. The thickness of the created layer can not be less than 200 mm. But the problem may be related to the low rigidity of the substrate being formed. Therefore, there is no point in filling up rubble under the foundations of serious, responsible buildings. But under the economic blocks, barns such a decision is fully justified.
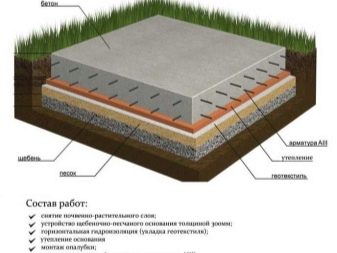
Concrete preparation layer is widely used under the plates and tapes. In addition to the increased bearing capacity, this is also due to the convenience of organizing these types of foundation on rigid underlying surfaces. This advantage is especially important in the winter months, when the characteristics of the soil deteriorate dramatically.
According to standard rules, pre-concreting is carried out strictly solutions from M-350 and above.
How to choose?
No matter how carefully the footing is made, the drainage, if the type of the main foundation is chosen incorrectly, all these works and constructions will be almost useless. When the construction site is composed of easily moving wet clay or dusty sand, prone to deep freezing, you should not choose a strip foundation. As soon as spring comes, the frosty swell will be replaced by lowering.This will inevitably lead to the occurrence of cracks and even fractures. Worst of all, even an immediate repair of all the rules with the use of adequate tools and materials will already be powerless.
But if there are no such problems with soils, the tape has a clear advantage - accelerated installation even without the help of professionals. Therefore, it is recommended to consider it primarily for a residential house, courtyard buildings and baths. Monolithic strip foundation of concrete is able to work up to 150 years, and at the same time everyone will be able to mount it without even spending money on renting powerful construction machines. The fee for the tape is very high, and you can not mount it in the cold months.
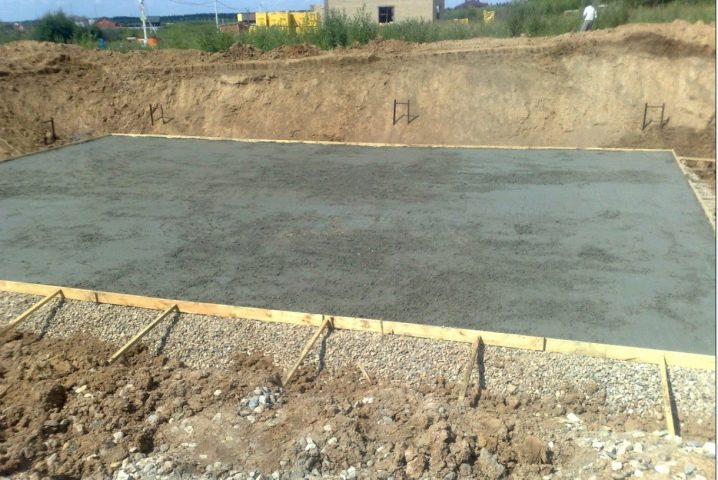
Problematic soils that occur quite often, especially in areas of new development, are easy to “win” using a slab. The speed of its installation at the same level of preparation is the same as that of the tape base. Slab substrates confidently fill in for 1-2 months on their own. More precisely, pouring is faster, but it takes a long time for the mixture to freeze. During the ascent and descent, the buildings on the slab move evenly, and this eliminates the danger of their destruction.
The monolithic structure can be mounted both on the surface and with some penetration; the benefits are crossed out at a significantly increased cost.
The solution to the problem of complex soil is possible at the expense of piles. Their bored-out type is mounted exclusively with the help of special equipment, and a very diverse one - both concrete transfer systems, forklifts, and boring machines will be required. If you plan to build a clay castle around the pile supports, you will have to pump it with special pumps. Of course, the use of a whole fleet of vehicles and the involvement of several professionals significantly increases the cost of construction work.
If the goal is to reduce costs and labor intensity, you can use a screw design.
Calculations
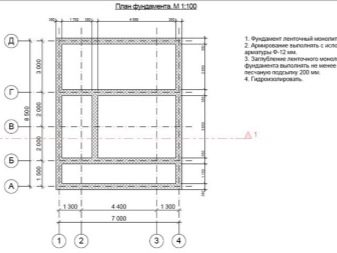
The foundation drawing is prepared only after all the necessary calculations and calculations of linear and strength parameters have been completed. External images are recorded separately, the overall scale is from 1: 100 to 1: 400. To transfer the scheme to the terrain it was easier, use axial marking. It is imperative to note in the documentation the gap from the extreme to the center axes.Another essential element of any well-thought scheme is a grid of coordinates.
During the calculations, the following parameters are calculated:
- the degree of penetration into the soil;
- section geometry;
- width of the supports of the tape;
- diameter and internal thickness of piles.
What is important, according to the results of well-performed calculations, it becomes clear which types and brands of building materials should be applied in a particular case. Experienced developers always lay a certain reserve for all indicators related to durability and stability. Even if it is not used immediately, it will at least help correct errors, extinguish the consequences of the growth of loads over time, and delay the critical depreciation of the structure.
The drawing should show what kind of footing is used and how it is organized. Equally significant is the demonstration of the points of entry of engineering systems and the description of their technical capabilities.
The sections should show:
- external contours of support blocks;
- blind area (for external walls);
- water protection equipment;
- the size of the ledges, if the foundation or its parts are mounted unevenly in height.
The tape bases are drawn with the indication of levels, it is possible to increase the visibility of such marks by putting marks with a turn away from a specific section.For the zero mark on any foundation scheme take the plane of the floors of the first floor. Additionally, they demonstrate the soil surface, basement line and cuts. The point of the cross section of the ribbon on the main plan is marked by broken strokes and arrows indicating the direction. To perform sections choose scales 1: 20, 1: 25 and 1: 50.
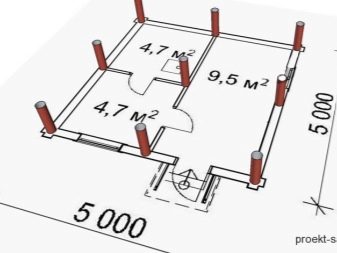
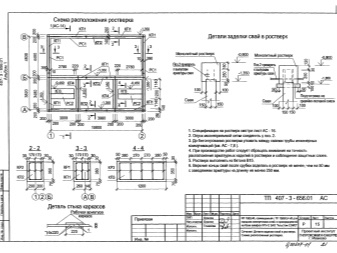
Professional builders, preparing the drawings, add to them the general specification of all the parts under the zero mark, the load table, assembly plans for prefabricated supports and a list of additional notes. Piles are placed under the outer walls around the perimeter, and the inner bearing walls are placed on supports. The gap from one leg to the other, in whatever direction the countdown is conducted, can be a maximum of 3 m.
If you plan to create a grillage, a separate scheme of such a design is created. Together with it, specifications or explanatory notes on materials are being prepared.
The height of the foundation increases, if you plan to form a base. Accurate information about its value can be found in building codes. In any case, the base should rise 100 mm above the calculated level of the maximum predicted snow mass. Ribbons, even in places where there is no snow or very little, should have a height of 0.3 m.The distance to the sewage is reflected in the cross-sectional street profile, it is coordinated with the placement of a different underground infrastructure.
In order to make communication as correct as possible, we should not forget about the considerations of convenience during layout, inspection and repair of networks. It is also recommended to take into account the need to protect adjacent pipelines, to separate cables from each other. Another consideration is maintaining the preservation of foundations and underground facilities, ensuring the tightness of water supply networks.
Pressure piping should be located 5 m from the base of the house, and non-pressure piping - at least 3 m. If you have to do the intersection of the water mains and sewage, the drainage channel should be placed below.
Stages of construction
The construction of a private house with their own hands at the stage of foundation works, in turn, falls into a number of phases.
First of all, it turns out the type of suitable technology, in which repel from:
- general condition of the soil;
- freezing lines;
- the height of the standing of groundwater.
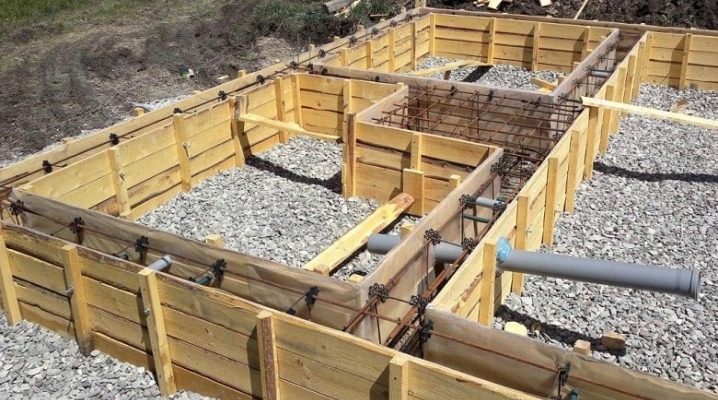
Special reference editions are used when working, but it is much more correct to do a full-fledged geological study.Regardless of the technical nuances, any step-by-step instruction provides for the installation of waterproofing and drainage of water. Monolithic foundations are placed by pouring concrete solution in the formwork.
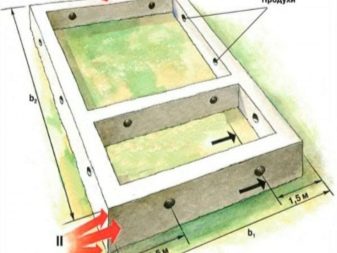
Tapes are created by digging trenches, while manufacturing them is divided into the following stages:
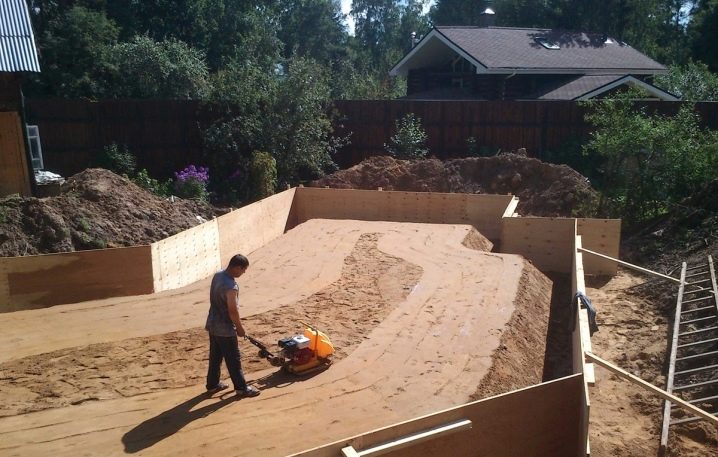
- clearing and compaction of the foundation pit;
- erection of a sand or gravel bed;
- laying hydraulic protection;
- checking the vertical walls;
- placement of reinforcement cages and filling the formwork with concrete;
- formwork removal and external waterproofing.
Build a columnar foundation will have to be different. Soil taken to a depth of 100 to 300 mm, removing the mounds, falling asleep pit soil. Horizontal lines are checked by building levels. The poles are placed at the intersection of the walls; these basting lines are used for digging holes and installing formwork. Then comes the turn of laying vertical reinforcement and pouring concrete into the formwork.
Collected mechanical strength of the pillars are covered with strapping. If you build small houses and outbuildings, you can use support columns made of wood. But it needs preparation due to the use of antiseptic mixtures.
The formation of monolithic bases has its own characteristics. The first step in the work is carefully prepared and cleaned from dirt site. Determine whether you need equipment for work, it is possible by the magnitude of construction work. Correctly make the pit of the same depth as the foundation line. The base of the trenches is supposed to be compacted, covered with sand and rammed, seeking to eliminate the smallest voids. A thin layer of concrete is poured over the sand mass, into which reinforcement is introduced and waterproofing is applied. On dry days, the surface is poured over with water, and covered with precipitation.
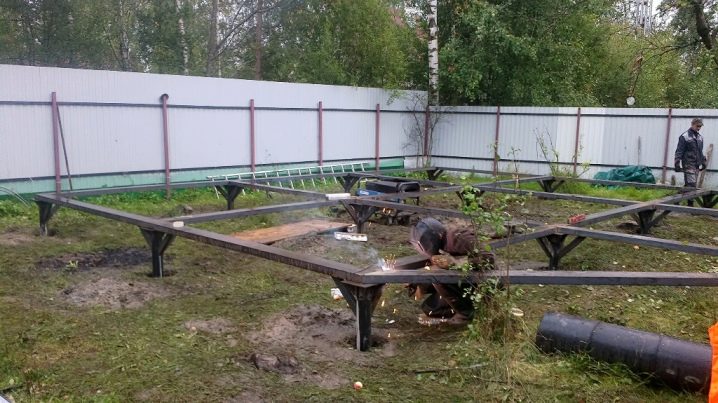
Pile foundations are represented by various types; Residential buildings on terrain with difficult terrain should be placed on screw piles. The diameter is calculated from the load that is created. Stakes are pounded in selected places, a basting is used to make pits. Screw bearings are screwed using pipe segments or a specialized tool.
It is necessary to check whether the above-ground fragments of piles coincide with each other, if necessary, the excess metal or concrete is cut off.
Tips and tricks
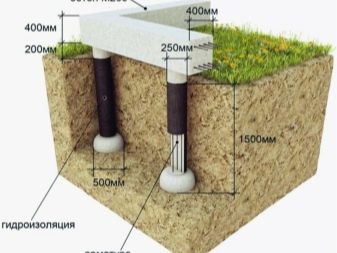
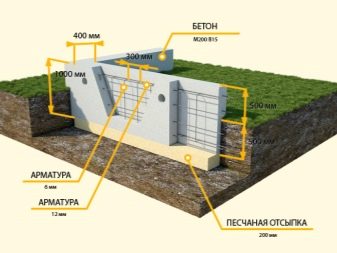
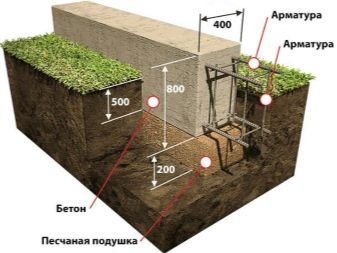
It is recommended to make a strip foundation from concrete structures of category B22.5. To get them, take 1 share of cement M-200, 2 parts of coarse sand and 2.5 shares of gravel. As an armature for it should be used rods made of steel with a section of 0.8-1.2 cm. Installation of shallow tape is recommended for the construction of one-story houses on stable soils. A prerequisite for success is the location of the support above the ground freezing line.
To align all the lines, you need to use a laser level; Special attention is paid to the verification of corners, the deviation in them is even worse than in the geometry of straight sections of the walls. Under the bath and the economic block it is impossible to make a foundation with a width of less than 250 mm; on heaving soils (silty) and on sandy mass the minimum value is 500 mm. If a high-grade one-floor house is being built, these parameters are 400 and 800 mm. The embedded part is designed to connect the blocks for the foundation, but also flight of stairs, wall panels, and floor structures can be attached to it. Any type of commercially produced metal can be used as embedded parts.
There are special techniques that allow you to build a foundation on a site with a high level of water. First of all, a drainage system should be constructed, which only avoids damage to building structures and their subsidence. Piles or precast concrete also protect against water, but using them is very expensive and difficult. Particular attention should be paid to the socle and the nuances of its execution. The wall of reinforced concrete is optimally combined with the piles, and with the tape - the continuation of the outer surface of the foundation.
Technology create a slab foundation of concrete, see the following video.