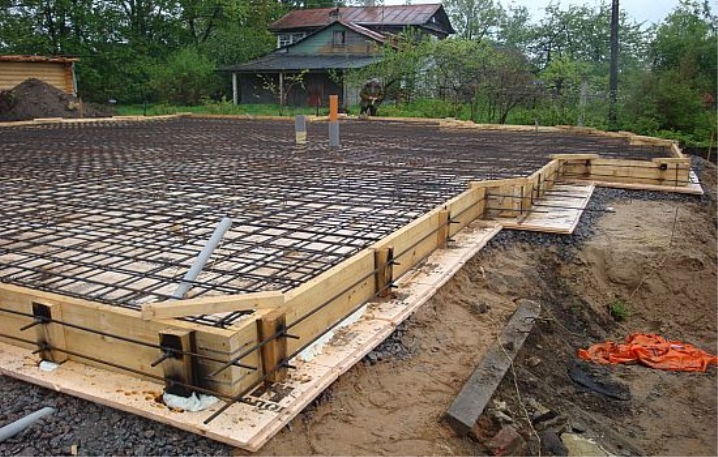
Non-buried foundation - types and uses
Non-buried foundation is used in the construction of light structures on heaving soils, the design of which allows a small structure without the formation of damage. It can also be used on coarse and rocky soils for the construction of structures made of stone. Its feature is that its main part is above ground level.
Kinds
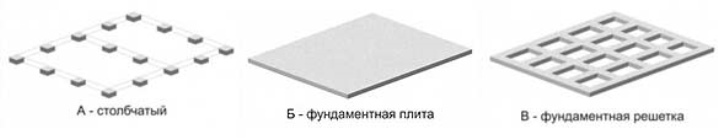
There are three types of non-buried foundations:
- columnar,
- monolithic plate,
- lattice.
Consider each view in more detail.
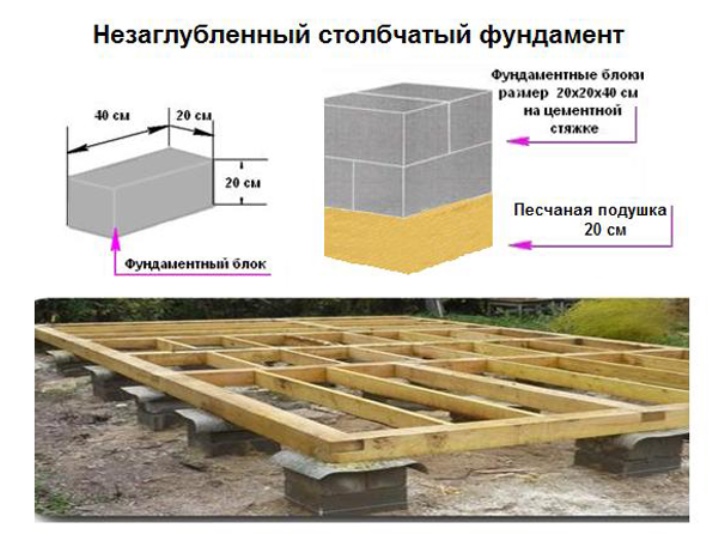
Columnar
Pillar is a cheap option that can withstand a light construction on soft soils or a heavy construction on very hard ones. This view is a short vertical support of about 25% of which is submerged in the ground in a pre-prepared burial.
The distance between the pillars should be from 1.5 to 2.5 meters.
Materials for creating pillars can be different:
- reinforced concrete,
- metal,
- wood,
- brickwork construction.
Wood requires pre-treatment to protect against rotting, cannot withstand a lot of weight, and therefore is rarely used, mainly for temporary buildings.
The column type is popular in private construction because of its reliability and simplicity of construction. However, it is suitable only for light buildings.
There is also the problem of overturning of individual or all supports. To eliminate this, the supports are made wide at the base and low in height. Also, this problem can be solved by removing the soil layer under the pole and replacing it with a sand pad.
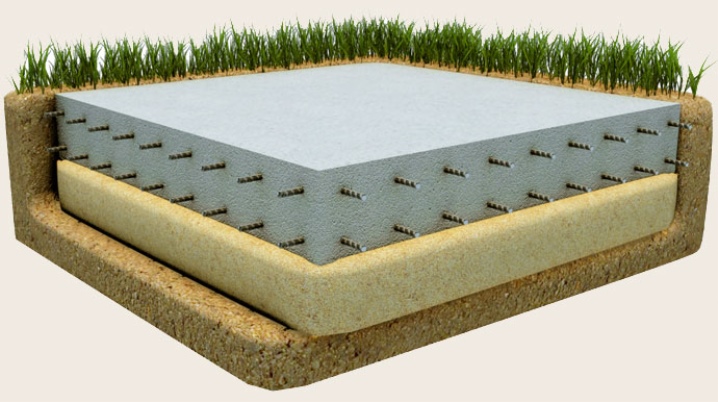
Monolithic plate
Monolithic slab is suitable for construction on solid soils on which there is no possibility of subsidence. Can also be used in permafrost conditions.
It is a solid concrete slab laid on the ground surface. The main problem arising from the operation of this type is the external forces acting on the stove, because it may collapse because of them.
On top of the stove will crush the house itself, so it should be easy.
When the soil freezes, it puts pressure on the stove from below. To prevent damage, several measures can be used both individually and in combination:
- increasing the thickness of the slab gives greater strength.
- reinforcement.
- use of heat-insulating materials under the plate. This will reduce the likelihood of soil freezing.
Lattice
The gridless non-submerged foundation consists of many small slabs. Between them the space is left which allows:
- save on material due to the fact that you do not need as much material as for a solid plate;
- since the plate is not solid, and then there is no destruction.
For formwork, you can use extruded polystyrene foam, it is not withdrawn after the concrete has dried, but is left as a heater. It is used exclusively on solid and slightly crouched soils, which does not allow its use in many cases. Also a disadvantage is the complexity of the installation of formwork and pouring concrete. Therefore, this type is not widely used.
In some cases, a non-buried foundation is suitable for building your own private house. And which type of existing is best suited, you need to choose individually in each case.