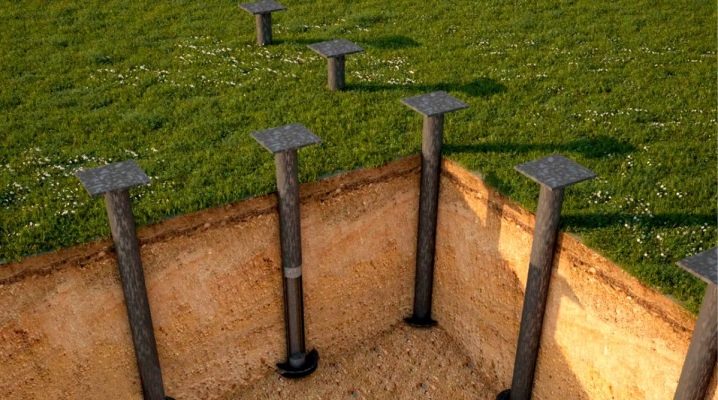
At what distance is it necessary to install screw piles?
Determining the distance between the piles in the construction of the foundation for a private house requires adherence to the methodology, which takes into account many factors. They include parameters that describe both the properties of the piles themselves, and the specifics of the soil and the weather conditions of the area. But the main point is the total load that the structure has on the foundation.
There are techniques for typical placement of piles, as well as rules that indicate the most loaded sections of the building. To determine the exact location of the piles, it is necessary to calculate their number and, following the instructions, place the supports in the plan of the foundation.
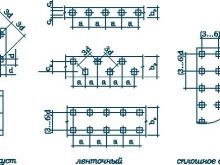
Specific location of piles depending on the type of foundation
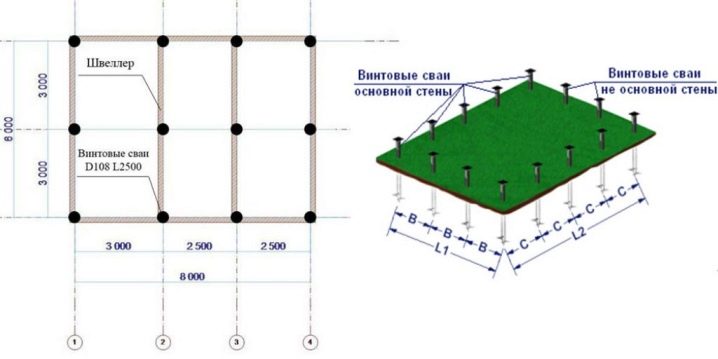
To determine the exact distance between the screw piles when building a frame or log houseit is necessary to make some calculations. Usually this distance ranges from 1 to 3 meters. During the construction of temporary or small non-essential buildings, it is calculated by eye, which is not allowed when designing permanent buildings.
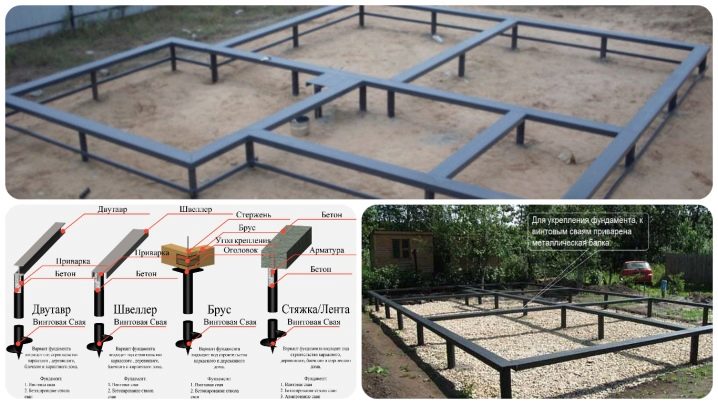
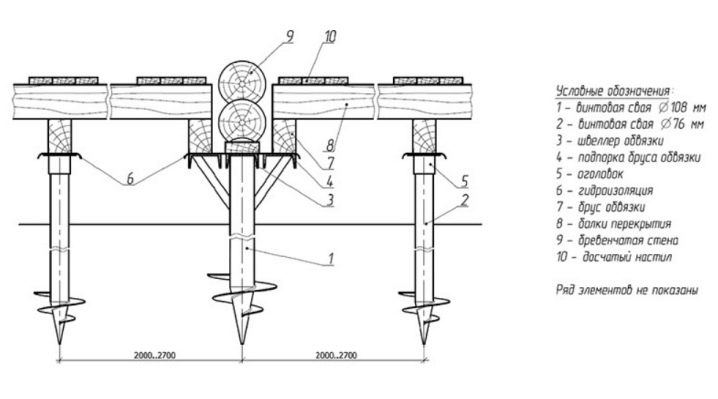
When finding the exact distance between the piles, the length of the beams of the grillage is taken into account, because they have two ends to rest against the tips of the screwed supports. This rule applies to frame and log houses, but it does not matter if the grillage is cast from concrete. In this case, the beams in it are simply not used.
When using slabs as a material for the foundation, the spacing between the screw piles is determined by the design documentation, taking into account their weight and structural features. In this case, the calculations become more complicated, but the principles of positioning the support beams remain the same - the piles must be installed under the bearing walls, at the entrance portal, under the columns, etc.
Options for the placement of piles and their purpose
Proper placement of piles is the basis of the integrity and durability of the foundation and the entire structure. When placing the supports, according to the load, it is possible to avoid critical areas that threaten the subsidence of piles and parts of the house.If the building has complex contours, the placement of supports requires special attention.
To this end, developed several basic techniques.
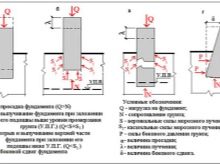
- Single occupancy. Piles are installed under the supports of frame structures, in the corner joints of the walls and under all bearing elements. However, their interval can not be more than 3 meters.
- Tape placement. The piles are located under the bearing walls with the difference from the single type, that the interval of their location is noticeably reduced and often amounts to only half a meter. This technique is used when it is necessary to withstand a large load (for example, a heavy 2 or 3-story building).
- Spray accommodation. This type is necessary to maintain heavy single or group structures. There is no definite step for this type, since often the piles are placed close to each other in a chaotic order corresponding to the load exerted. Their placement directly depends on the calculation of pressure zones. The only condition - the elements must be present around the perimeter and the area of the slab foundation for which they are supports.
- Solid placement or pile field. The supports are installed everywhere under the area of the slab foundation, the step is about 1 meter. This technique is used for massive buildings or on soils with a weak bearing capacity.
In the construction of standard frame private houses, not differing huge mass, almost always used a single or tape placement of piles.
Features of the calculation
When calculating the piling interval, certain essential criteria must be considered. This will allow not to have the elements too close, spending money in vain, and not to put them too far, exposing the foundation and the whole house to the danger of subsidence.
The following points are taken into account in the calculations of professional builders:
- the mass of the structure (frame, roof, decoration, etc.);
- the mass of internal filling (equipment, furniture, things and tenants);
- dynamic factors (wind load, snow weight on the roof in winter);
- soil bearing capacity;
- technical parameters of screw piles;
- safety factor.
To determine the payload when calculating the interval of placement of piles using the appropriate SNiP. For example, for a one-story residential structure, the load is set at 150 kg per 1 sq. Km. msquare Wind and snow load indicators are reference and are set for each region depending on local weather conditions. The safety factor is on average from 1.1 to 1.25.
Before planning the location of piles, it is necessary to calculate their number. It is determined based on the total support load. The total weight is divided by the bearing capacity of one pile, as a result of which the exact number of supports is found out. Then they are placed with equal intervals around the perimeter of the building and under the supporting structures.
The second option is the arrangement of piles, planned on the basis of determining the load on 1 linear meter of the grillage. To calculate it, it is necessary to divide the total load of the building by the total length of all load-bearing walls, and then divide by the bearing capacity of the selected type of piles. The result is an indicator that determines the required number of supports to support the 1-meter grillage. After that, the required interval for the placement of piles is determined, sufficient to maintain the foundation. This method is used for more massive buildings and is rarely used for low-rise frame houses.
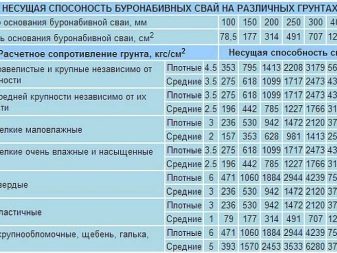
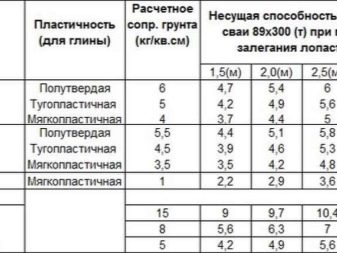
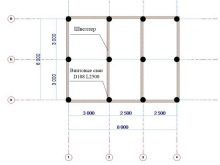
To determine the approximate bearing capacity of piles of a particular type, you need to look at the table with the relevant indicators. More accurate information used in the final calculations is indicated by the manufacturer in the specification for a particular product. It should be borne in mind that the minimum distance at which the piles are screwed for the house and the terrace is 108 cm.
Rules for the location of screw piles under the foundation
In order to maintain the structure and ensure uniform load, the supports should be placed according to the established order in places with the greatest load.
The following zones can be distinguished:
- in the corners of the connection of the facade walls;
- at the points of intersection of supporting walls and interior partitions;
- near the entrance opening;
- on the internal area with an interval of not more than 2 meters;
- under the stove or fireplace (2 piles or more);
- under the supporting wall, on which there is an additional construction like a balcony or mezzanine, locally increasing the load on the wall.
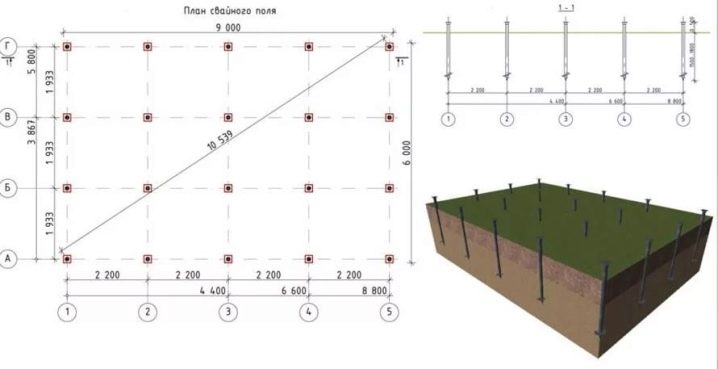
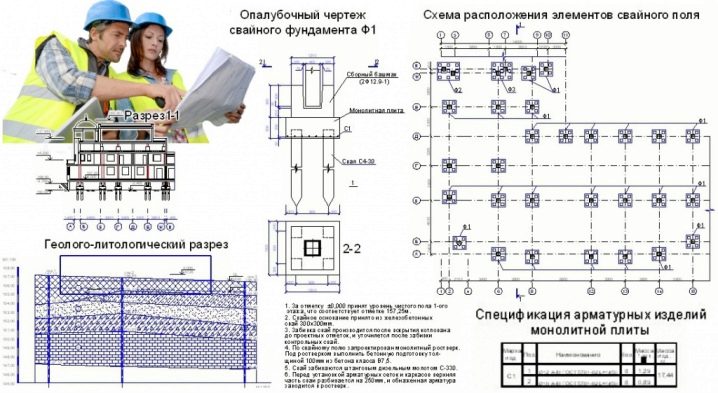
After finding the exact number of piles, a stage of schematic arrangement of the supports in terms of the foundation begins. In this case, the above rules for their placement under the bearing elements and at critical points of the structure should be taken into account.The balance should be evenly spaced between the key supports. So is determined by the step in the arrangement of screw piles.
Pile counting example
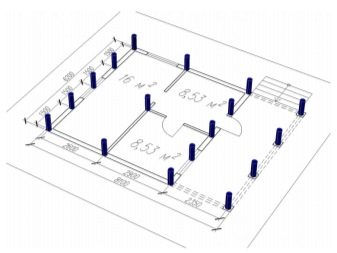
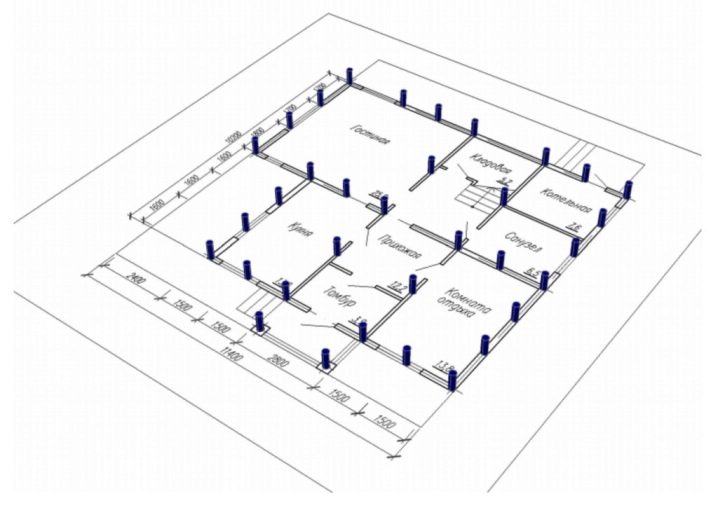
Consider the features of the calculation on the example of a square-shaped house with a 8x8 perimeter.
Other features of the building include:
- frame type, slate roof, porch;
- basement dimensions - 8x8, the height of the structure - 3 meters;
- the house has 3 rooms, formed by the intersection of a solid wall 8 meters long and partitions 4 meters long;
- the frame is made of 150x150 timber, the grillage - 200x200;
- the walls are covered with sandwich panels.
Calculation of the area of the walls:
- outdoor - 8 * 3 * 4 = 96 square meters. m;
- internal - 8 * 3 + 4 * 3 = 36 square meters. m
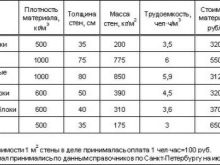
Calculation of the mass of the walls when using table values for a mass of 1 square. m:
- external (bearing) - 50 * 96 = 4800 kg;
- partitions - 30 * 36 = 1080 kg;
- the total weight is 4800 + 1080 = 5880 kg.
Calculation of the mass of the basement and attic floors using tabular values for a mass of 1 square. m:
- ground floor - 8 * 8 * 150 = 9600 kg;
- attic - 8 * 8 * 100 = 6400 kg;
- the total weight is 9600 + 6400 = 16000 kg.
To determine the mass of the additional load (internal filling of the house: finishing materials, things, equipment), the table value 350kg / 1kv is used. When calculating the load for a two-story house, the weight of the additional load is multiplied by 2.
8 * 8 * 350 = 22400 kg.
Calculation of the total load on the foundation:
16000 + 22400 = 38400 kg.
Calculation of the number of piles by the formula K = P * K / S, where:
"P" - the total load;
“K” is the reliability coefficient (in the example, 1.4);
“S” is the maximum load per 1 pile (this value is based on the specificity of the pile, in the example it is a support with a diameter of 300 mm).
Soil resistance is determined by the specifics of the area on which the house is being built. In the example, this is a soil with an average density of 3 kg. / cc see, weak freezing of 1 meter and deep groundwater.
38400*1.4/2600=20.6
Based on the calculation, we can conclude that in this case, you need to use 21 piles.
The given example shows a possible variant of calculations. It does not take into account the specific specifics of the individual structure, which may affect the final number of piles and their placement in the plan of the foundation.
One of the main points - finishing materials and other stuff at home, which is about half the load. The table value is based on the average weight of the materials. If massive plating is used, for example, slabs of granite or marble, masonry of stone or brick, etc., the overall load indicator may change significantly.In such circumstances, an accurate calculation of the weight of all elements related to the additional load is indispensable.
For pile foundations and recommended spacing between piles, see this video.